Microstructure and electrochemical corrosion behavior of Q460 axle shell submerged arc weld
-
摘要:
选取Q460低合金高强钢及其埋弧焊焊接接头,采用金相显微镜、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、能谱仪(EDS)和显微硬度计等测试手法研究焊缝组织及性能;通过电化学极化曲线的测试研究焊缝腐蚀行为。试验结果表明,焊缝组织为针状铁素体和珠光体,经过淬火加高温回火后的焊缝晶粒最为细小;焊缝的硬度大于母材的硬度;焊缝的抗腐蚀性能低于母材,在质量分数为3.5%的NaCl腐蚀环境下,较于同为低合金高强钢的Q510和Q345,Q460焊缝耐腐蚀性也略差。
Abstract:Q460 high strength low alloy steel and its submerged arc welded joints were chosen to study microstructure and properties of weld by metallographic microscope, scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) and microhardness tester. Corrosion behavior of weld was studied by electrochemical polarization curve test. The experimental results showed that microstructure of weld was needle-like ferrite and pearlite, grains of weld were the finest after quenching and high temperature tempering. Hardness of weld was greater than that of parent material. Corrosion resistance of weld was lower than that of parent material. Corrosion resistance of Q460 weld was slightly worse than that of Q510 and Q345 high strength low alloy steel in the corrosion environment NaCl with a mass fraction of 3.5%.
-
0. 前言
随着制造业的迅速发展, 汽车产业的发展已成为当今推动中国经济发展的中坚产业。在整个汽车配件制造中, 汽车车桥是所有汽车配件中至关重要的一个大部件[1]。车桥的作用是承受汽车的载荷,维持汽车在道路上的正常行驶,而车桥壳体的焊缝质量是影响内部零件质量的关键[2 − 3]。
埋弧焊是电弧在焊剂覆盖下,在焊丝与母材间燃烧的一种熔焊方法,与焊条电弧焊、钨极氩弧焊和搅拌摩擦焊等焊接方法相比,其操作环境好,焊缝成形美观、质量好、生产效率高、投入成本低[4 − 7]。基体组织为“铁素体 + 珠光体”的Q460是一种典型的低合金高强(High strength low alloy, HSLA)钢,具有较高的强度和良好的塑韧性,广泛应用于矿山机械、压力容器、车辆船舶、桥梁和建筑等行业[8 − 10]。
使用电化学测试法研究金属的腐蚀行为,是目前来说比价普遍的。目前,开路电位法、极化曲线法和电化学阻抗法是研究腐蚀行为的经典方法,国内外的学者基本都利用了上述方法研究焊缝的腐蚀行为。Deen等学者[11]利用极化曲线法测不同试样的金属焊接不同区域的自腐蚀电位和自腐蚀电流,发现焊缝相较于母材区会更容易发生腐蚀;唐君等学者[12]和林海威[13]通过研究金相图,利用电化学测试,分析了金相组织及极化曲线等,得到了焊缝的腐蚀趋势和腐蚀速率, X80管线钢的母材耐蚀性优于焊缝,焊缝会优先发生腐蚀。祝李洋[14]通过研究焊缝区域的微生物腐蚀行为,使用了电化学测试法,通过测量开路电位,极化曲线等得到了不同条件下的腐蚀结果。伊红伟等学者[15]通过电化学方法研究了异种金属焊缝电偶腐蚀,通过使不同金属偶接,得到了不同金属的抗腐蚀能力大小的对比。张苏强[16]研究了Q315耐蚀钢弧焊接头腐蚀行为,通过电极化测量法,分析了不同区的腐蚀性能的差异及耐蚀性差异的原因。
目前,关于Q460钢埋弧焊焊缝组织、性能及腐蚀行为的研究报道较少。该研究对Q460车桥壳埋弧焊焊缝进行多项分析测试,并进行电化学试验研究腐蚀的开路电位、极化曲线,深入了解焊缝的组织及耐蚀性能,通过测量其不同区域的硬度,分析其性能。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验母材使用14 mm厚的Q460低碳钢,焊丝选用直径为1.2 mm的H08A,采用MIG打底+埋弧焊焊接,母材和焊丝的化学成分见表1。车桥埋弧焊设备及其焊接前后对比如图1所示。
表 1 母材和焊丝的化学成分(质量分数,%)材料 C Si Mn P S Mo Ti Cr Ni Q460 0.079 0.21 0.82 0.011 0.0013 0.19 0.091 — — H08A ≤0.10 ≤0.03 0.3~0.5 ≤0.03 ≤0.03 — — ≤0.2 ≤0.3 1.2 测试方法
线切割选取母材和优质焊接接头。首先,对未经热处理的试样进行腐蚀抛光,随后进行金相观察。然后,使用线切割机将观察完的试样切成三等份,随后进行热处理,对试样采用如下的热处理方式:①900 ℃正火(保温2 h),空冷;②900 ℃回火(保温2 h),炉冷;③920 ℃淬火(保温2 h),水冷后,630 ℃回火(保温30 min),空冷。粗磨、精磨、抛光及5%硝酸 + 95%酒精腐蚀后用金相显微镜观察金相组织。
试样断裂后,用扫描电子显微镜进行焊缝微观形貌的观察,并用能谱仪进行母材及焊缝产物的元素分析。最后用硬度计测量母材及焊缝的硬度。
电化学测试选取母材和优质焊接接头。试验环境为质量分数3.5%的NaCl溶液,采用三电极系统与CS电化学工作站相连,进行数据采集、开路电位和极化曲线分析。比对3种不同低合金高强钢焊缝的耐腐蚀能力。
1.3 模型与网格
车桥建模和网格划分均采用ABAQUS软件,其桥壳模型如图2a所示,网格划分如图2b所示。桥壳模型进行适当分割以区分出上、下桥壳部分和焊缝部分,对其焊缝部分进行网格细化,对非焊缝部分进行网格密过渡。
2. 测试结果分析
2.1 金相组织
图3为不同热处理工艺下Q460焊接接头的宏观形貌及微观形貌。图3a为Q460焊接接头的宏观形貌,可以看出焊缝和母材有很明显的分界,焊缝被腐蚀的更强。图3b为未经过热处理的焊缝微观组织,它的组织为铁素体加珠光体,深色为珠光体,亮色为铁素体。图3c为经过了正火处理的焊缝微观组织,发生了伪共析转变,产生了伪共析体。图3d为经过了退火处理后的焊缝组织,形成了片状的珠光体,晶粒较为细小。图3e为经过淬火 + 高温回火的焊缝组织,形成了回火索氏体,晶粒相较于退火更加细小。图3f为母材经过了淬火 + 高温回火的组织,也形成了回火索氏体,不过晶粒相较于焊缝更加粗大。
2.2 SEM微观形貌
图4为焊缝SEM微观形貌。左侧为填充区,右侧为母材区。图4b中,方框区域内暗区域为铁素体,亮色区域为渗碳体,黑色圆点为焊接气孔缺陷;图4c中,方框区域内片状组织为片状珠光体,暗色为铁素体。在组织物形态与分布方面,焊缝为大量细小的针状铁素体及珠光体,因此,焊缝的硬度可能会大于母材的硬度;母材的珠光体是铁素体和渗碳体以薄层形式交替重叠形成的混合物,为分布均匀的片状珠光体。
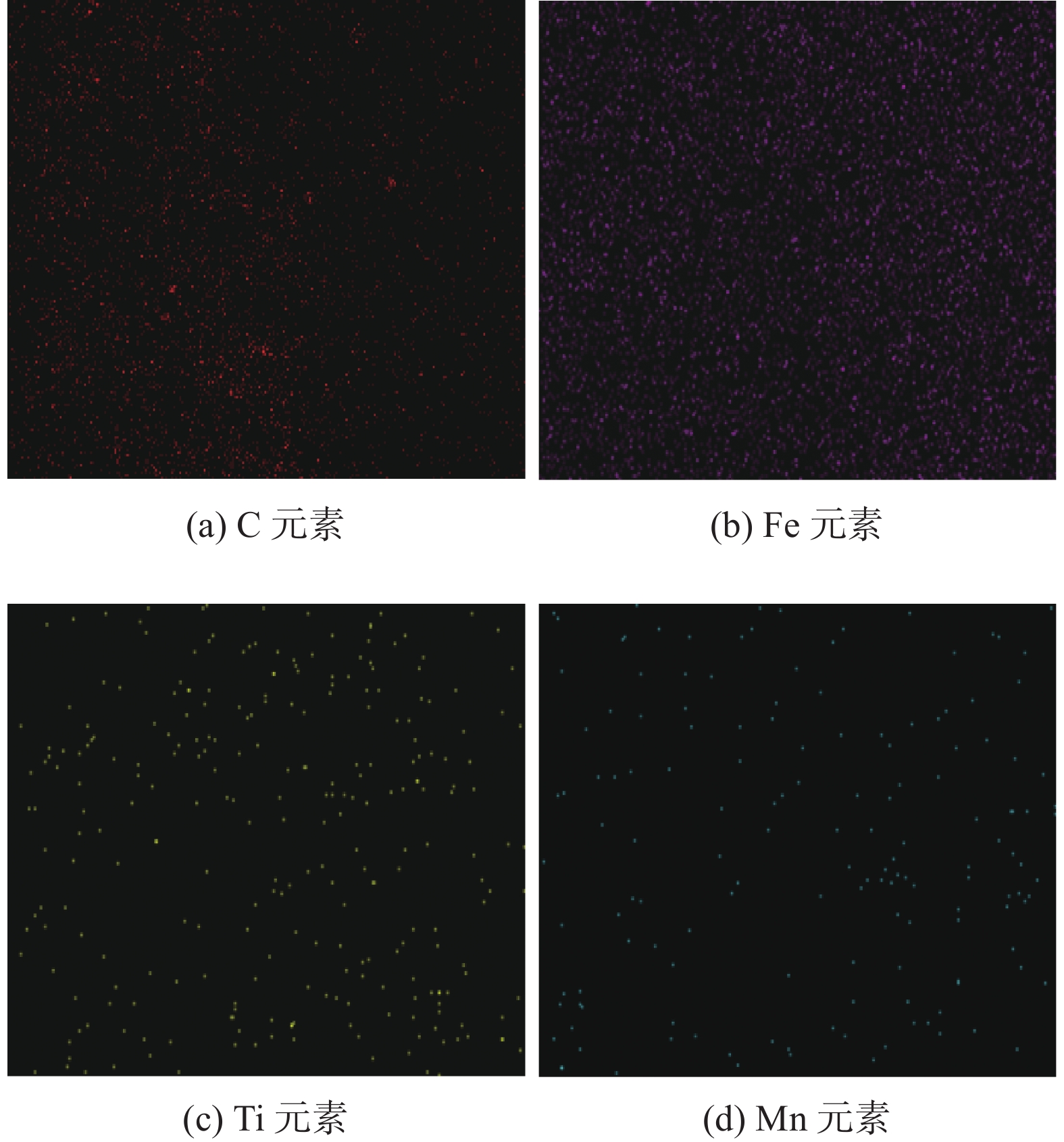
2.3 EDS能谱
图5为焊缝和母材的能谱图。图6为主要元素C,Fe,Mn,Ti分布图。由图可知C元素主要集中于焊缝,焊缝的C元素含量明显高于母材,而Fe元素的含量略低于母材,焊缝的Mn和Ti元素较为集中均匀。可见,焊缝的硬度会大于母材的硬度。
2.4 显微硬度
图7为焊接接头显微硬度分布。母材平均显微硬度为168 HV,焊缝平均显微硬度为217 HV。焊缝的显微硬度明显高于其他区域,主要由于焊缝晶粒明显细化,细小的针状铁素体和贝氏体使显微硬度明显提高,显微硬度结果与上述分析一致。
2.5 极化曲线
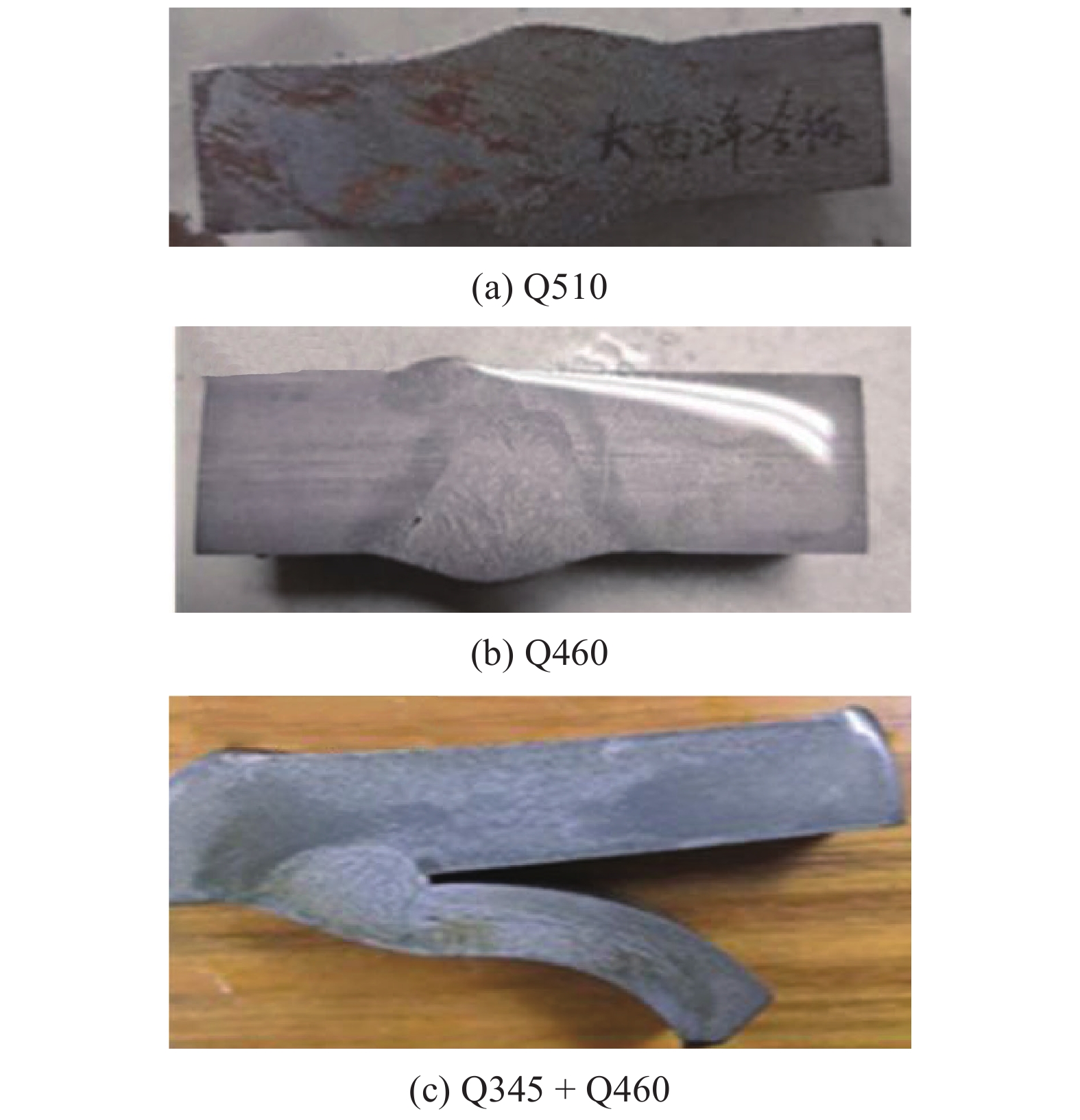
图8为Q460及同为HSLA钢的Q510以及Q345 + Q460焊接接头宏观形貌。
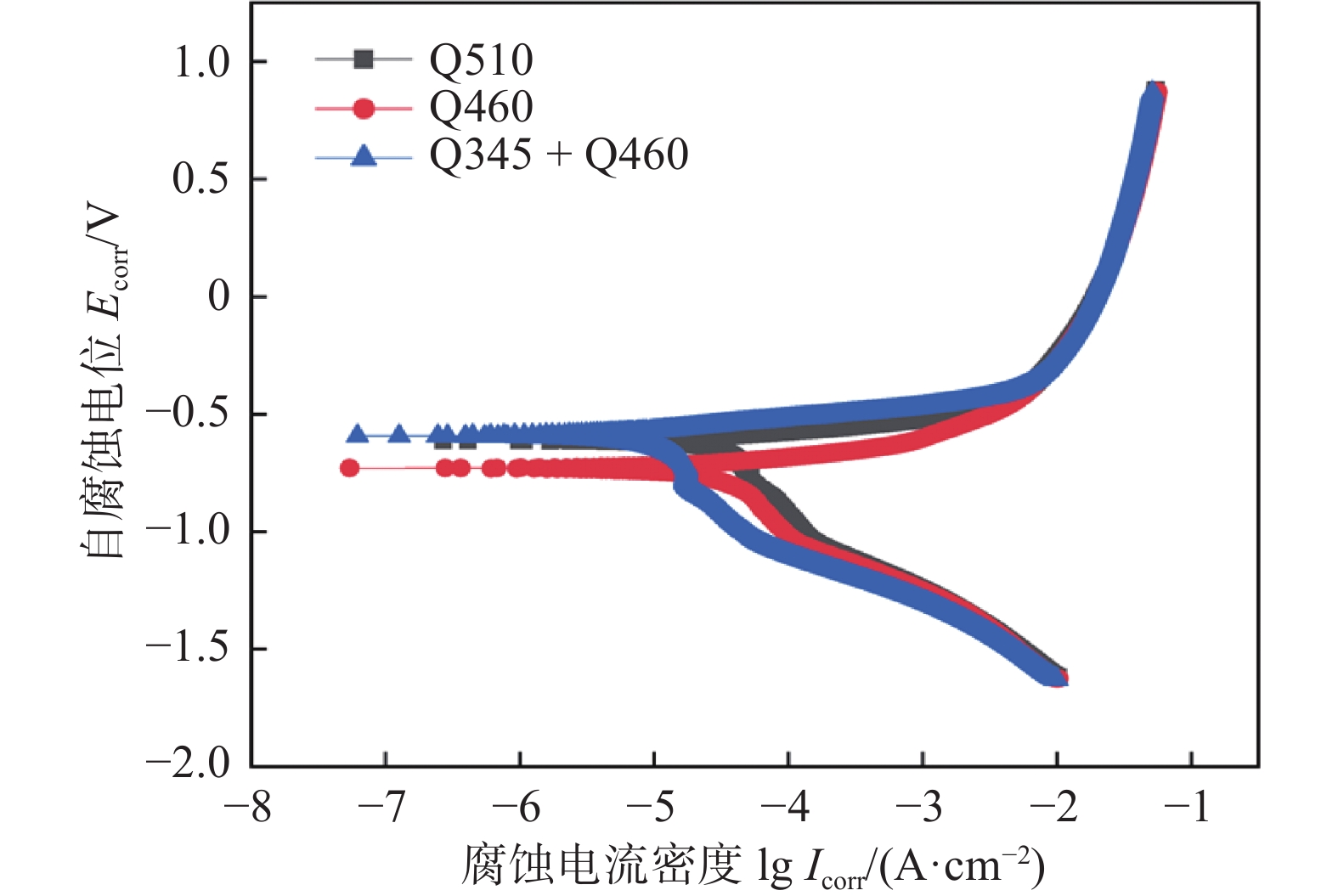
对3种焊接接头进行电化学极化试验,分析3.5%的NaCl溶液腐蚀环境下材料的自腐蚀特性。图9为3种HSLA钢焊缝的极化曲线。进行Tafel拟合可以得到焊缝相应的自腐蚀电位(Ecorr)和腐蚀电流密度(Icorr),表2为极化曲线的电化学参数。可以看出Q460钢焊缝的电流密度最大。而腐蚀的电流密度越大,试样的耐腐蚀性就越差,被腐蚀的倾向就越大。所以可以得出耐腐蚀能力由小到大为:Q460,Q510,Q460 + Q345。同样的,可以通过观察自腐蚀电位,来比较耐腐蚀能力的大小。自腐蚀电位越小,耐腐蚀能力越差,由图9和表2可以看出,Q460的自腐蚀电位为−729.94 mV且最小,Q345 + Q460的自腐蚀电位最大,所以根据自腐蚀电位的大小来判断耐腐蚀的能力的话,耐腐蚀能力由小到大为:Q460,Q510,Q460 + Q345。由此可见,Q460焊缝的耐腐蚀性在同类低合金高强钢中略差。
表 2 极化曲线的电化学参数接头 腐蚀电流密度Icorr/(A·cm−2) 自腐蚀电位Ecorr/mV Q460 4.382 6 × 10−5 −729.94 Q510 3.874 9 × 10−5 −614.58 Q345 + Q460 1.568 2 × 10−5 −592.44 3. 仿真模拟分析
3.1 焊接过程模拟
车桥焊接模拟温度场及应力场分别如图10和图11所示。分别模拟单个焊枪焊接、2个焊枪同向移动焊接、2个焊枪异向移动焊接3种焊接过程的温度变化和应力变化。对比3种焊接过程的温度场可得,单热源焊接的整体温度最低,双热源同向焊接与双热源异向焊接的整体温度相近,均高于单热源焊接。双热源同向焊接的温度分布上下对称,但左右不对称;双热源异向焊接的温度分布不仅上下对称,而且左右对称。因此,在保证较高焊接效率的情况下,双热源异向焊接更适合于桥壳的埋弧焊工序。对比3种焊接过程的应力场可得,3种焊接的应力值相差不大,但应力分布情况差异明显。单热源焊接的应力分布最为不均匀;双热源同向焊接的应力分布相对均匀,但在桥壳左右分布不均;双热源异向焊接则能够获得整体较为均匀的应力分布。结合温度场情况可得,双热源异向焊接更适合于桥壳的埋弧焊工序。
3.2 焊接腐蚀仿真
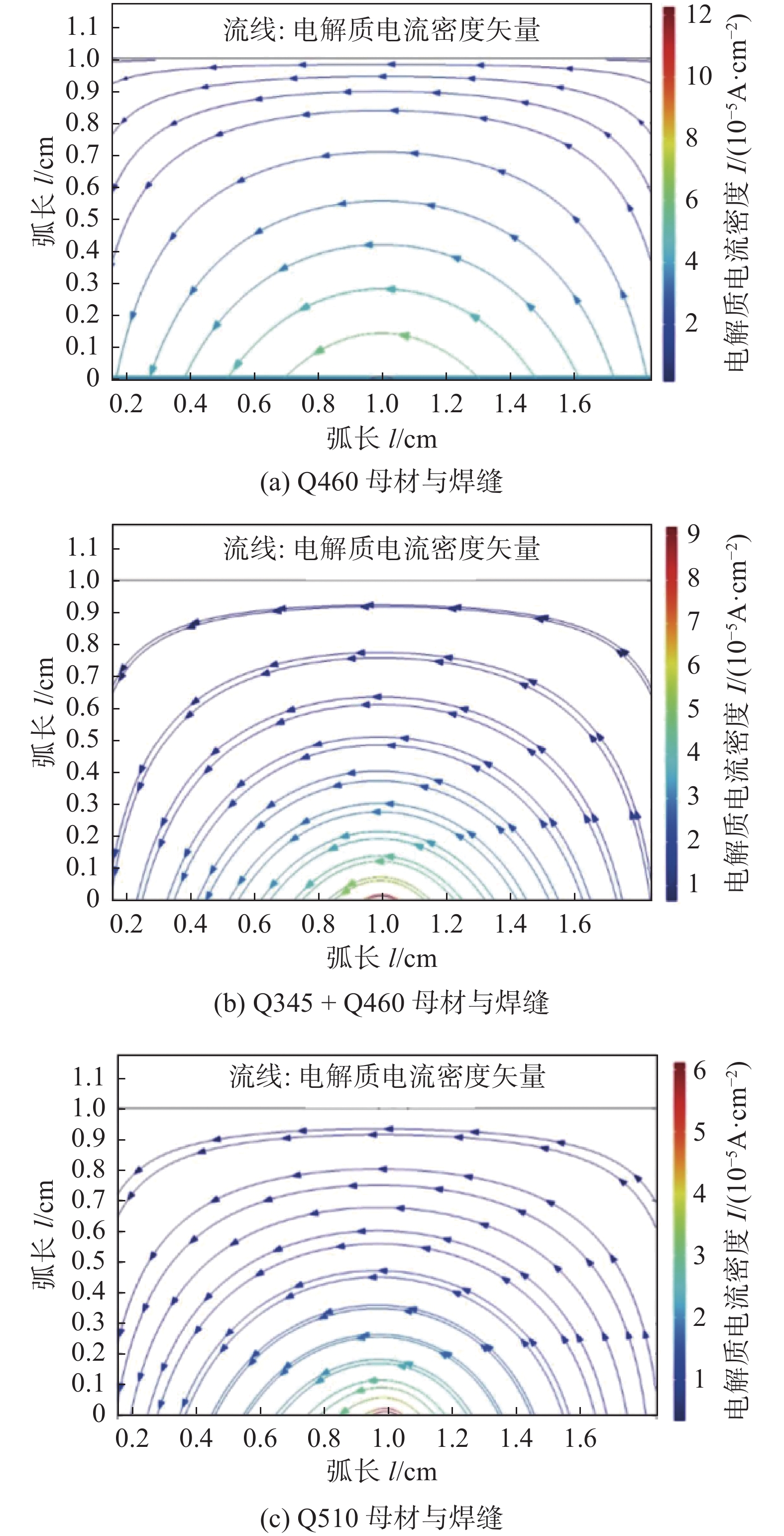
焊接腐蚀仿真主要探究了电解质中的电位与电流密度的分布,腐蚀仿真结果如图12和图13 所示。3种钢的母材与焊缝发生电偶腐蚀的电解质电位分布如图12所示。由于3种电偶腐蚀模型的设计较为平均,所以电解质中的电位分布通过颜色图例显示较为相似,其主要差别在图例数值上。通过图例数值可见,焊缝的电位较高,母材电位较低,其中Q460电解质电位最高,Q510电解质电位次之,Q345 + Q460电解质电位最小。由于腐蚀效果越剧烈电解质电位越高,故推测Q460的抗蚀能力较弱,Q510适中,Q345 + Q460抗蚀能力较强。3种钢的母材与焊缝发生电偶腐蚀的电解质电流密度如图13所示。由电解质电流密度矢量的方向可以得知,电流由阳极表面流向阴极表面,故焊缝为阳极,母材为阴极,焊缝优先发生腐蚀。根据电解质中的电流密度,电流密度最大区域在两者的接触位置发生最强烈腐蚀,因此根据图例中的数据可得3种不同的电偶腐蚀模型的抗腐蚀能力大小,其抗蚀能力顺序与电位分布结果相符。
4. 结论
(1)焊缝主要由细小的针状铁素体和珠光体组成。
(2)母材平均显微硬度为168 HV,焊缝平均显微硬度为217 HV,焊缝显微硬度大于母材显微硬度。
(3)热处理前,焊缝组织为珠光体 + 铁素体;经过正火处理后,组织为伪共析体;经过退火处理后,组织为细片状珠光体;淬火 + 高温回火后,组织为回火索氏体。另外,淬火加高温回火后的焊缝晶粒最为细小。
(4)焊缝的耐腐蚀能力低于母材,在3.5%NaCl腐蚀环境下,相较于同为低合金高强钢的Q510和Q345,Q460焊缝的耐腐蚀性略差。
-
表 1 母材和焊丝的化学成分(质量分数,%)
材料 C Si Mn P S Mo Ti Cr Ni Q460 0.079 0.21 0.82 0.011 0.0013 0.19 0.091 — — H08A ≤0.10 ≤0.03 0.3~0.5 ≤0.03 ≤0.03 — — ≤0.2 ≤0.3 表 2 极化曲线的电化学参数
接头 腐蚀电流密度Icorr/(A·cm−2) 自腐蚀电位Ecorr/mV Q460 4.382 6 × 10−5 −729.94 Q510 3.874 9 × 10−5 −614.58 Q345 + Q460 1.568 2 × 10−5 −592.44 -
[1] 孙景刚, 刘政军, 樊继师, 等. 汽车车桥直焊缝焊接设备控制系统的研制[J]. 焊接, 2007(11):53 − 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2007.11.014 [2] 赵正彩. 汽车焊接桥壳成型工艺的分析对比[J]. 重型汽车, 2009(3):18 − 21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-211X.2009.03.006 [3] 杨启杰, 龚胜峰. 车桥壳体机器人焊接工艺优化研究[J]. 金属加工(热加工), 2020(8):40 − 43. [4] 杨越, 李亚军, 郭容, 等. 06Cr20Ni11钢埋弧焊焊缝的显微组织和性能[J]. 机械工程材料, 2020, 44(2):18 − 21, 72. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202002004 [5] 朱敏, 张延松. X80埋弧焊热影响区的微观组织与局部软化行为分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(4):69 − 73, 96. [6] 刘斌, 刘云, 牛辉, 等. 裂纹及气孔对多丝埋弧焊焊缝冲击韧性的影响[J]. 焊接, 2021(11):42 − 47. [7] Brijpal Singh. Influence of flux composition on microstructure and oxygen content of low carbon steel weldments in submerged arc welding[J]. China Welding, 2018, 27(1):10 − 19.
[8] 魏巍, 孙屹博, 杨光, 等. 基于能量耗散的Q460焊接接头疲劳强度评估[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(4):49 − 55. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200907001 [9] 朱海洋, 刘川, 邹家生. 超声冲击对Q460高强钢焊接接头残余应力及组织性能的影响[J]. 焊接, 2018(8):11 − 13. [10] 魏巍, 邹丽, 杨鑫华. 基于能量耗散的Q460焊接接头S-N曲线快速预测[J]. 焊接, 2021(4):13 − 18. [11] Deen K M, Ahmad R, Khan I H, et al. Microstructural study and electrochemical behavior of low alloy steel weldment[J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31:3051 − 3055. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.01.025
[12] 唐君, 刘峰. X80钢焊接接头在酸性模拟液中的电化学腐蚀[J]. 辽石油化工大学学报, 2011, 31(4):60 − 63. [13] 林海威. X80管线钢焊缝区腐蚀行为研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2014. [14] 祝李洋. X80管线钢及其焊缝组织的微生物腐蚀[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳理工大学硕士学位论文, 2020. [15] 伊红伟, 胡慧慧, 陈长风, 等. CO2环境下油酸咪唑啉对X65钢异种金属焊缝电偶腐蚀的抑制作研究[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2020, 40(2):96 − 104. doi: 10.11902/1005.4537.2019.209 [16] 张苏强. Q315NS耐蚀钢弧焊接头腐蚀行为研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士学位论文, 2019. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 曲之国,王东明,王立志,赵和明,杨海峰. 40 mm厚度Q500MC钢板大热输入焊接试验. 机械制造文摘(焊接分册). 2024(03): 16-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: