Physical characteristics of VPPAW arc for thick plate aluminum alloys
-
摘要:
为克服厚板铝合金穿孔焊接熔池极易失稳的难题,该研究从厚板焊接时电弧温度场出发,旨在探究厚板穿孔焊接熔池稳定性的机理。通过建立三维数值模型,研究了焊接母材厚度分别为5 mm和16 mm下变极性等离子电弧的温度场、流场和电流密度分布。结果表明,随着板厚的增加,变极性等离子电弧温度场分布发生改变,5 mm板厚电弧温度的衰减情况为线性,而16 mm厚板焊接的电弧温度衰减情况为二次型,使得温度变化更加复杂。变极性等离子弧焊接5 mm厚度铝合金时,整个小孔熔池的电流密度呈1.0 × 106 A/m2以上,但是在焊接16 mm厚板铝合金时,相同电流密度仅达到小孔深度的12 mm处。该研究有望对实现大厚度铝合金稳定焊接,拓宽变极性等离子弧焊接应用范围提供理论指导。
Abstract:In order to overcome the problem of easily unstable molten pool in thick plate aluminum alloys perforation welding, this study started from arc temperature field during thick plate welding, aiming to explore mechanism of molten pool stability of thick plate piercing welding. By establishing a three-dimensional numerical model, temperature field, flow field and current density distribution of variable polarity plasma arc (VPPA) with 5 mm and 16 mm thickness of welding base metal were studied. The results showed that with the increase of plate thickness, temperature field distribution of VPPA changed. Arc temperature decay of 5 mm plate thickness was linear, while that of 16 mm plate welding was quadratic, which made temperature change more complicated. When welding 5 mm thick aluminum alloy plates by VPPAW, current density of the entire keyhole molten pool was above 1.0 × 106 A/m2, but when welding 16 mm thick aluminum alloy plates, the same current density only reached 12 mm depth of the small hole. This study was expected to provide theoretical guidance for realizing stable welding of large thickness aluminum alloy and broadening application range of VPPAW.
-
0. 前言
对于大型结构件,将钢板结构换成密度小的铝合金结构,重量可以减轻至少50%,因此,铝合金材料特别适用于向轻量、高速化转型的制造业。随着铝合金材料及工程制造业的不断发展,10 mm以上大厚度铝合金在工程结构中的应用需求逐渐增加。大厚度铝合金的焊接制造成为金属材料成形制加工领域亟待解决的关键问题。而焊接热输入增加导致的气孔、变形、焊接未熔合、夹杂及焊接接头软化等焊接缺陷严重制约了大厚度铝合金在各工程制造业的应用。变极性等离子弧与其他焊接方法相比,具有造价低、环境适应能力强、维修成本低、焊缝质量高、焊后变形小及单面焊双面成形等优势。尤其对于厚板的焊接,变极性等离子弧焊接技术有着较大的潜力[1 − 7]。
Zhang等学者[8]在VPPA穿孔焊接过程中采用脉冲激光视觉检测法研究3 mm 厚不锈钢焊缝背面的小孔形状尺寸,研究发现:小孔稳定形成时,小孔的宽度就不会随着焊接电流和焊接速度的变化而变化。Short等学者[9]在研究变极性等离子弧平板焊接时发现:在对不同厚度的薄板进行焊接时,焊缝的尺寸随着喷嘴的直径增大而增大,熔深减小;随着试板的厚度增加时,维持熔池稳定的工艺区间变窄。Shinoda等学者[10]研制出新型大电流等离子弧焊接系统用来焊接 15 mm厚 A5052 铝合金,通过模拟软件模拟出合适的电流波形,得到了提高热输入及焊接系统的控制方法,焊缝成形质量显著提高。
陈桂芳[11]研究了8 mm厚2A14高强铝合金变极性等离子弧穿孔横焊熔池行为,建立了横焊小孔熔池的受力模型,分析了表面张力和其他力之间的关系,通过改变喷嘴的结构,提出了“柔弧”的概念,降低电弧压力同时改善了焊缝成形。韩永全[12]自行研制的以80C196Kc为核心的变极性等离子弧焊接设备,分析了变极性等离子弧电弧特性,电弧产热机理,同时进行了不同厚度高强铝合金的焊接工艺试验,得出不同厚度的工艺试验窗口。
目前,变极性等离子弧焊在8 mm以下的铝合金焊接已实现了良好效果,工艺规范相对成熟[13 − 15]。但对于更大厚度的铝合金,若要实现稳定的高质高效焊接,仍然存在一定的难度。板厚增加热输入相应提高,导致接头弱化严重。熔池液态金属量增加,形成的气泡数量增多,出现气孔缺陷的概率增加。穿孔熔池处于高拘束状态,大量液态金属在强烈的等离子射流作用下,流动特性更加复杂,小孔熔池稳定建立难度增加。因此,需要进行厚板焊接时电弧与熔池之间相互作用机制的深入研究,探明小孔熔池稳定性机理,获得变极性等离子电弧热力输出特性,形成新的适宜大厚度铝合金的焊接工艺体系,对实现大厚度铝合金优质高效焊接,拓宽变极性等离子弧焊接应用范围,提高过程稳定性及可重复性都具有重要的理论指导意义和工程实用价值。
该文建立了VPPA的三维模型和预置小孔三维模型。对比了5 mm和16 mm不同板厚下VPPA的温度分布,研究了等离子电弧中轴线温度衰减变化。为了探究整个焊接周期变极性等离子弧的规律,对不同极性下VPPA温度场进行了比较。结合5 mm和16 mm不同板厚下变极性等离子电弧物理场分布和温度衰减变化,讨论了厚板工艺的传热机理。
1. 数值模型及试验方法
1.1 材料种类和焊接条件
5 mm和16 mm厚铝合金变极性等离子弧焊接工艺参数分别见表1。钨极直径4.8 mm,喷嘴直径4.0 mm。铝合金均为A5052,尺寸分别为150 mm × 500 mm × 5 mm和150 mm × 500 mm × 16 mm。该焊接系统由北京工业大学自制交流等离子弧焊电源与NW-300ASR,日本东京新日铁焊接工程有限公司研发的焊枪,2个氩气瓶分别用于提供等离子体和保护气体,自主搭建的卡具工装等。
表 1 铝合金VPPA穿孔焊接工艺参数板厚
b/mm离子气体流速
Q1/(L·min−1)保护气体流速
Q2/(L·min−1)EP电流
I/A交流频率
f/HzEN时间占比
η(%)弧高
h/mm钨极内缩
l/mm焊接速度
v/(mm·s−1)5 4.0 18.0 130~150 40 70 2.0 4.0 3.0 16 3.5 18.0 480~500 40 70 4.0 4.0 2.1 1.2 计算区域
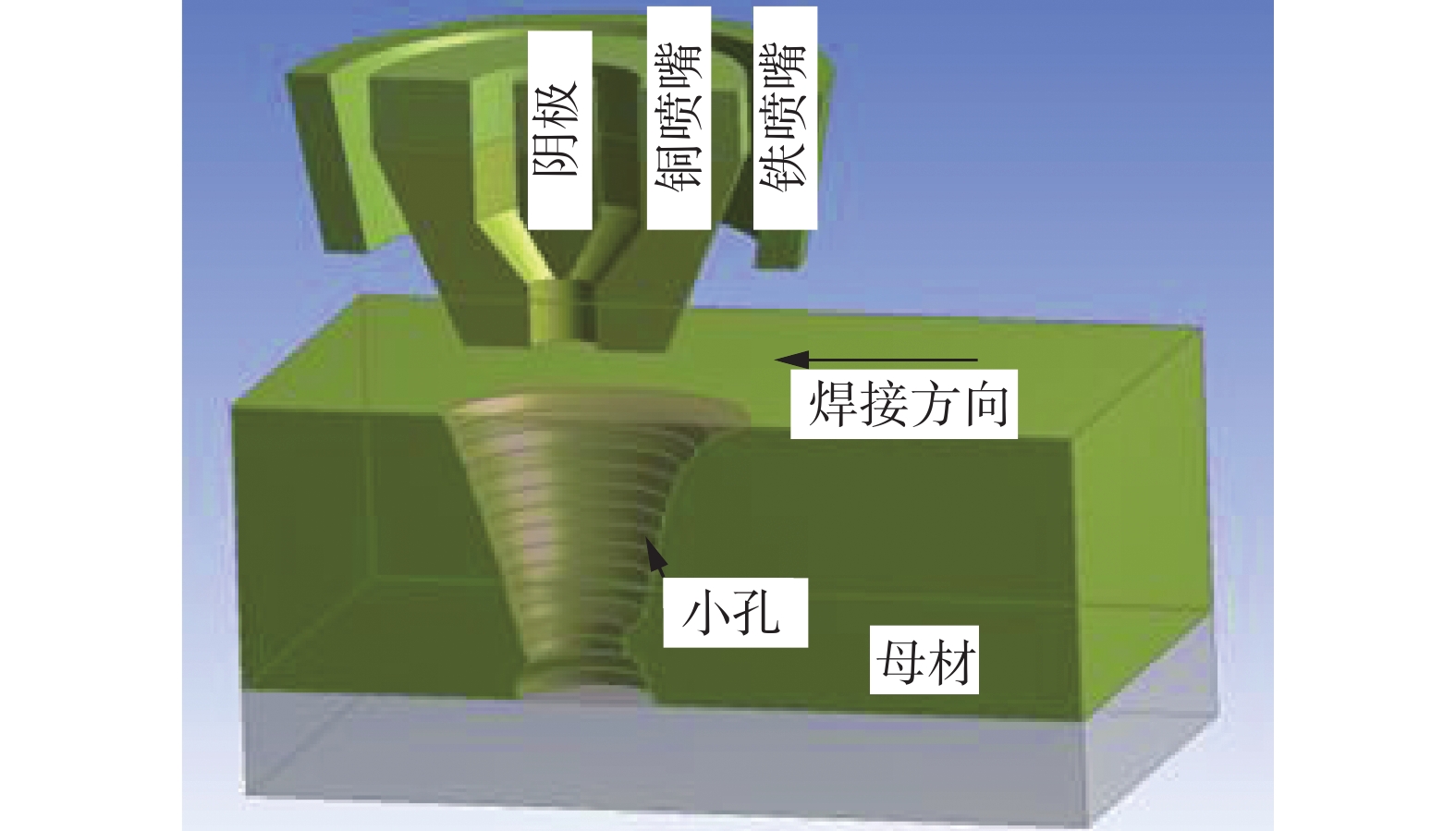
图1为电弧模型的计算域。钨极、喷嘴和母材为固体区域,其余为流体区域。母材的材质设定为铝。工件上的电位都是0 V。边界条件根据实际制造工艺。
1.3 计算参数
模拟条件与试验中的参数相同,见表1。通过设置钨极的电流密度,可以计算不同的电流值。
1.4 磁流体动力学模型
提出以下假设:①等离子电弧处于局部热力学平衡;②忽略粘性耗散;③等离子弧是轴对称的;④等离子弧为连续介质。基于上述假设,控制方程描述如下:
质量守恒方程
$$ \dfrac{\partial \rho }{\partial t}+\rho \mathrm{d}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{v}\boldsymbol{v}=0 $$ (1) 动量守恒方程
$$ \dfrac{\partial (\rho u)}{\partial t}+\rho \mathrm{d}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{v}\left(u\boldsymbol{v}\right)={J}_{y}{B}_{{\text{z}}}-{J}_{{\text{z}}}{B}_{y}-\dfrac{\partial P}{\partial x}+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial x}\left\{\mu \left[2\dfrac{\partial u}{\partial x}-\dfrac{2}{3}\left(\dfrac{\partial u}{\partial x}+\dfrac{\partial v}{\partial y}+\dfrac{\partial w}{\partial {\text{z}}}\right)\right]\right\}+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial y}\left[\mu \left(\dfrac{\partial u}{\partial y}+\dfrac{\partial v}{\partial x}\right)\right]+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial {\text{z}}}\left[\mu \left(\dfrac{\partial w}{\partial x}+\dfrac{\partial u}{\partial {\text{z}}}\right)\right] $$ (2) $$ \dfrac{\partial \left(\rho v\right)}{\partial t}+\rho \mathrm{d}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{v}\left(v\boldsymbol{v}\right)={J}_{{\text{z}}}{B}_{x}-{J}_{x}{B}_{{\text{z}}}-\dfrac{\partial P}{\partial y}+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial y}\left\{\mu \left[2\dfrac{\partial v}{\partial y}-\dfrac{2}{3}\left(\dfrac{\partial u}{\partial x}+\dfrac{\partial v}{\partial y}+\dfrac{\partial w}{\partial {\text{z}}}\right)\right]\right\}+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial {\text{z}}}\left[\mu \left(\dfrac{\partial v}{\partial {\text{z}}}+\dfrac{\partial w}{\partial y}\right)\right]+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial x}\left[\mu \left(\dfrac{\partial v}{\partial x}+\dfrac{\partial u}{\partial y}\right)\right] $$ (3) $$ \dfrac{\partial \left(\rho w\right)}{\partial t}+\rho \mathrm{d}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{v}\left(w\boldsymbol{v}\right)={J}_{x}{B}_{y}-{J}_{y}{B}_{x}-\dfrac{\partial P}{\partial {\text{z}}}+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial {\text{z}}}\left\{\mu \left[2\dfrac{\partial w}{\partial {\text{z}}}-\dfrac{2}{3}\left(\dfrac{\partial u}{\partial x}+\dfrac{\partial v}{\partial y}+\dfrac{\partial w}{\partial {\text{z}}}\right)\right]\right\}+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial x}\left[\mu \left(\dfrac{\partial w}{\partial x}+\dfrac{\partial u}{\partial {\text{z}}}\right)\right]+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial y}\left[\mu \left(\dfrac{\partial w}{\partial y}+\dfrac{\partial v}{\partial {\text{z}}}\right)\right] $$ (4) 能量守恒方程
$$ \dfrac{\partial \left(\rho {c}_{\rm p}T\right)}{\partial t}+\rho {c}_{\rm p}\mathrm{d}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{v}\left(T\boldsymbol{v}\right)=\dfrac{\partial }{\partial x}\left(\dfrac{k}{{c}_{\rm p}}\dfrac{\partial T}{\partial x}\right)+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial y}\left(\dfrac{k}{{c}_{\rm p}}\dfrac{\partial T}{\partial y}\right)+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial {\text{z}}}\left(\dfrac{k}{{c}_{\rm p}}\dfrac{\partial T}{\partial {\text{z}}}\right)+\dfrac{{J}_{x}^{2}+{J}_{y}^{2}+{J}_{{\text{z}}}^{2}}{\sigma }{-S}_{\mathrm{R}} $$ (5) 式中:v为流体速度;div v 为流体速度v 的散度;ρ为密度;t为时间;u, v, w分别为3个方向上的速度分量;Jx, Jy, Jz分别为3个方向上的电流密度;Bx, By, Bz分别为3个方向上的磁感应强度分量;P为压力;μ为粘度系数;cp为比热容;k为热导率;T为流体的温度;SR为辐射损失。
洛伦兹力项在动量守恒方程中,焦耳热项在能量守恒方程中,它需要求解磁感应强度B和电流密度J。因此,需要求解麦克斯韦方程组:
欧姆定律
$$ {J}_{x}=-\sigma \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial x} \text{,} {J}_{y}=-\sigma \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial y} \text{,} {J}_{{\text{z}}}=-\sigma \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial {\text{z}}} $$ (6) 电流连续性方程
$$ \dfrac{\partial }{\partial x}\left(\sigma \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial x}\right)+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial y}\left(\sigma \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial y}\right)+\dfrac{\partial }{\partial {\text{z}}}\left(\sigma \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial {\text{z}}}\right)=0 $$ (7) 磁矢势的泊松方程
$$ -{\nabla }^{2}{A}_{x}={\mu }_{0}{J}_{x} \text{,} -{\nabla }^{2}{A}_{y}={\mu }_{0}{J}_{y} \text{,} -{\nabla }^{2}{A}_{{\text{z}}}={\mu }_{0}{J}_{{\text{z}}} $$ (8) $$ {B}_{x}=\dfrac{\partial {A}_{{\text{z}}}}{\partial y}-\dfrac{\partial {A}_{y}}{\partial {\text{z}}} \text{,} {B}_{y}=\dfrac{\partial {A}_{x}}{\partial {\text{z}}}-\dfrac{\partial {A}_{{\text{z}}}}{\partial x} \text{,} {B}_{{\text{z}}}=\dfrac{\partial {A}_{y}}{\partial x}-\dfrac{\partial {A}_{x}}{\partial y} $$ (9) 式中:σ为电导率;Ax,Ay,Az为3个方向上的磁矢量;μ0为真空磁导率。
在等离子弧与钨极的界面上,在EN阶段,阴极的附加源项包括热离子电子发射冷却、离子复合加热和辐射冷却
$$ {H}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{k}}=\left|{j}_{\mathrm{i}}\right|{V}_{\mathrm{i}}-\left|{j}_{\mathrm{e}}\right|{\varphi }_{\mathrm{k}}-\varepsilon \alpha {T}^{4} $$ (10) 在EP阶段,附加源项包括电子加热和辐射冷却
$$ {H}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}}=\left|j\right|{\varphi }_{\mathrm{a}}-\varepsilon \alpha {T}^{4} $$ (11) 在等离子弧与基板的交界面处,EN相中附加源项与EP相中钨极表面附加源项相同
$$ {H}_{\mathrm{b}\mathrm{a}}=\left|j\right|{\varphi }_{\mathrm{a}}-\varepsilon \alpha {T}^{4} $$ (12) EP阶段附加源项与EN阶段钨极表面的附加源项相同
$$ {H}_{\mathrm{b}\mathrm{k}}=\left|{j}_{\mathrm{i}}\right|{V}_{\mathrm{i}}-\left|{j}_{\mathrm{e}}\right|{\varphi }_{\mathrm{k}}-\varepsilon \alpha {T}^{4} $$ (13) 式中:ε为表面发射率;α为玻尔兹曼常数;φk为阴极的功函数;φa为阳极功函数;Vi 为Ar的电离势;je为电子流密度;ji 是离子流密度;$ \left|j\right|=\left|{j}_{\mathrm{e}}\right|+\left|{j}_{\mathrm{i}}\right| $为在电流连续性方程中计算得到的阴极表面的总电流密度。
这些方程的关键问题是确定电子的离子流的密度。当钨极(热阴极材料)为阴极时,一般采用理查德森电流密度理论分离$ {j}_{\mathrm{e}} $ 和$ {j}_{\mathrm{i}} $。$ {j}_{\mathrm{e}} $的值不能超过理查德森电流密度
$$ \left|{j}_{\mathrm{R}}\right|={A}_{\mathrm{c}}{T}^{2}\mathrm{exp}\left(-\dfrac{e{\varphi }_{\mathrm{e}}}{{K}_{\mathrm{B}}T}\right) $$ (14) 式中:${A}_{\rm c}$ 为阴极表面热离子发射常数;${\varphi }_{\mathrm{e}}$ 为电极表面在局部表面温度下热离子发射的有效功函数;KB为玻尔兹曼常数。如果$ \left|j\right| $>$ \left|{j}_{\mathrm{R}}\right| $,则假设$ {j}_{\mathrm{i}} $=$ \left|j\right|- $ $ \left|{j}_{\mathrm{R}}\right| $。
2. 结果与讨论
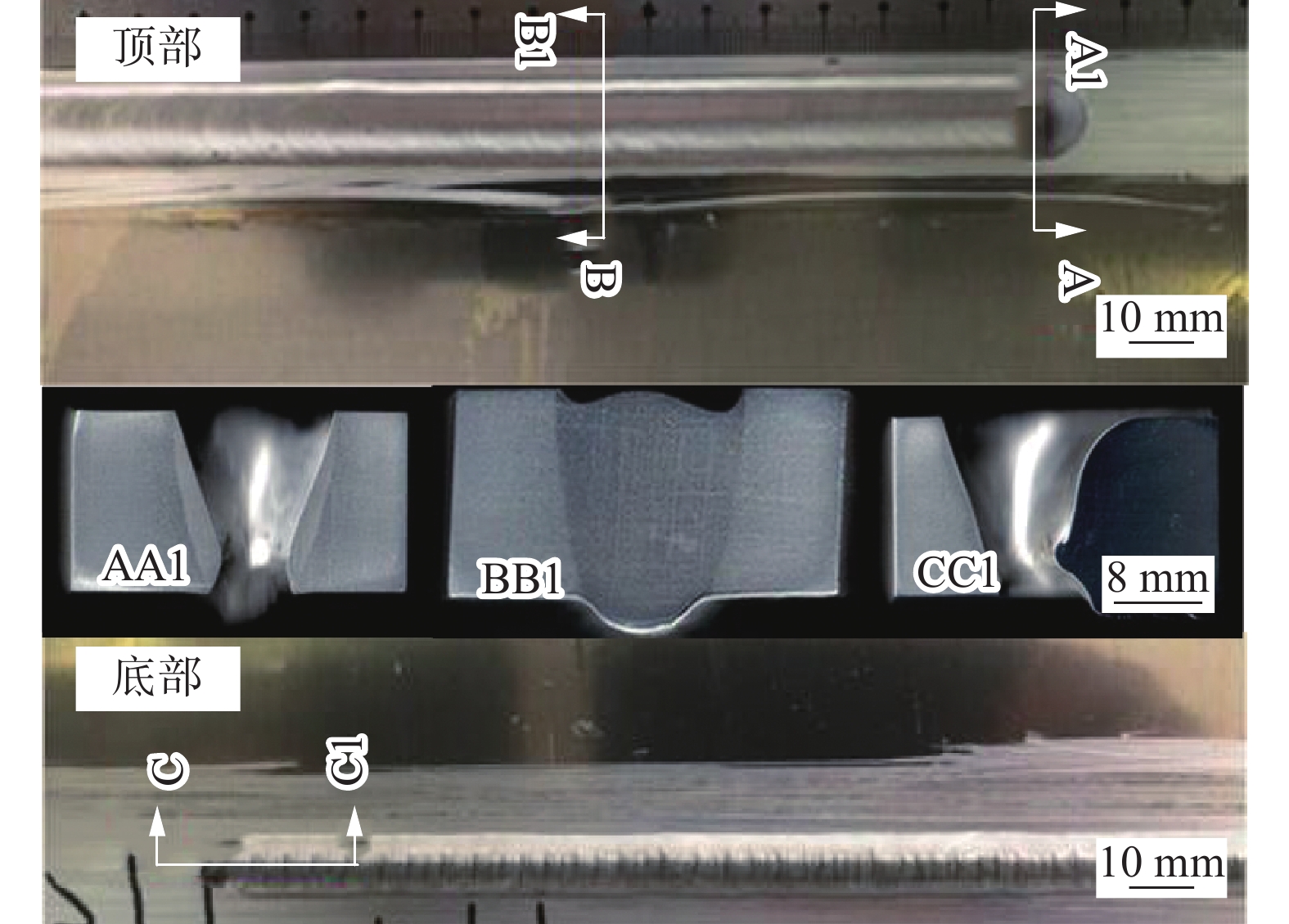
16 mm厚铝合金VPPA穿孔焊焊缝和小孔形貌如图2所示,AA1为小孔垂直于焊接方向截面,BB1为焊缝截面,CC1为小孔沿焊接方向截面。通过关闭等离子弧,小孔保留在焊缝的末端,再对小孔区域进行切割、研磨和蚀刻。其纵向截面的形状和尺寸与横向截面的形状和尺寸明显不同,表明它不是三维轴对称的。因此,在模拟穿孔焊接过程时应考虑这种不对称性。在AA1中,小孔顶部孔径为14.2 mm,底部孔径为7.8 mm;在CC1中,小孔顶部孔径为18 mm,底部孔径为8 mm。
图3为VPPA焊接不同厚度铝合金时电弧的温度分布。VPPA焊接5 mm铝板材时,电弧最高温度可达24 000 K,如图3a所示。VPPA焊接16 mm铝板材时,电弧最高温度可达37 000 K,如图3b所示。电弧温度高温区分布在喷嘴处,在小孔内部温度持续衰减。
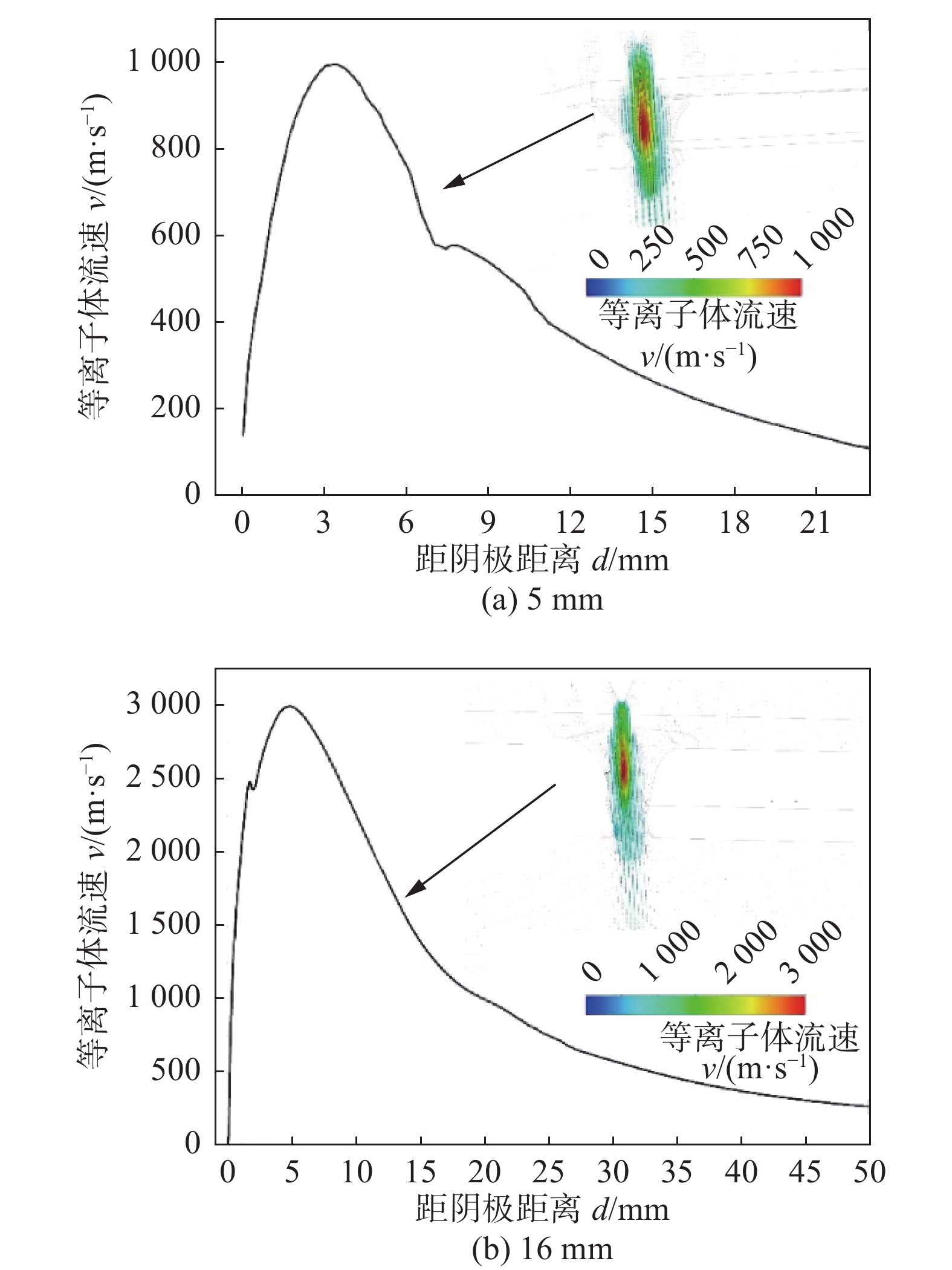
图4为不同厚度铝合金电弧等离子体的流速。图4a为变极性等离子弧焊接5 mm铝板材时等离子体流场情况,等离子体流速最大值为1 000 m/s,位于喷嘴内部,高温区也在此附近出现,可以得到在等离子体受到喷嘴压缩和高温加热的影响,使得速度及能量达到最大值;当等离子体进入已经穿孔的熔池,压缩程度骤然减小,温度也持续衰减,速度大幅度衰减。图4b为变极性等离子弧焊接16 mm铝板材时等离子体流场情况,等离子体流速最大值为3 000 m/s,位于喷嘴内部,高温区也在此附近出现,可以得到在等离子体受到喷嘴压缩和高温加热的影响,使得速度及能量达到最大值;当等离子体进入已经穿孔的熔池,压缩程度骤然减小,温度也持续衰减,速度大幅度衰减。高温影响离子气流速,温度越高等离子体运动越剧烈,流速越快。
图5为不同厚度铝合金等离子电弧电流密度分布。图5a为变极性等离子弧焊接5 mm铝板材时电流密度的分布情况,最大电流密度出现在钨极尖端附近。电流密度分布主要集中在等离子弧轴上,最大电流密度为1.5 × 108 A/m2。图5b为变极性等离子弧焊接16 mm铝板材时电流密度的分布情况,最大电流密度为4.0 × 108 A/m2。变极性等离子弧焊接5 mm厚铝合金时,电流密度为1.0 × 106 A/m2以上的区域几乎涵盖整个小孔熔池,但是在焊接16 mm厚板铝合金时此电流密度为1.0 × 106 A/m2以上的区域仅作用在12 mm处,并没有覆盖作用在整个小孔,电弧能量的衰减愈加剧烈。
上述中出现了随着板厚的增加,电流密度分布存在明显的差异情况,电流密度和产热呈正相关,也许是厚板焊接不易成形问题的关键所在。铝合金导电性能好,而变极性电弧工作中电流也会存在闭合回路,整个系统也符合基尔霍夫定律。由于电流对于母材来讲只有一侧产生电流,是非对称的,电流的流向和电流密度也肯定不是对称的。若是铝合金载流能力已经远远大于电流增加量,就会出现上述情况,电流在流经母材一定厚度的情况下,已经完成了实现电流回路的条件,底部的母材就会承担很少的载流,这种现象就会导致变极性等离子在厚板焊接时电流密度分布差异的主要原因。
在焊接过程中,工况相对于复杂多变,电弧形态不是空间对称,将垂直于板材平面的一条经过钨电极的尖端的法线作为此研究的中轴线。
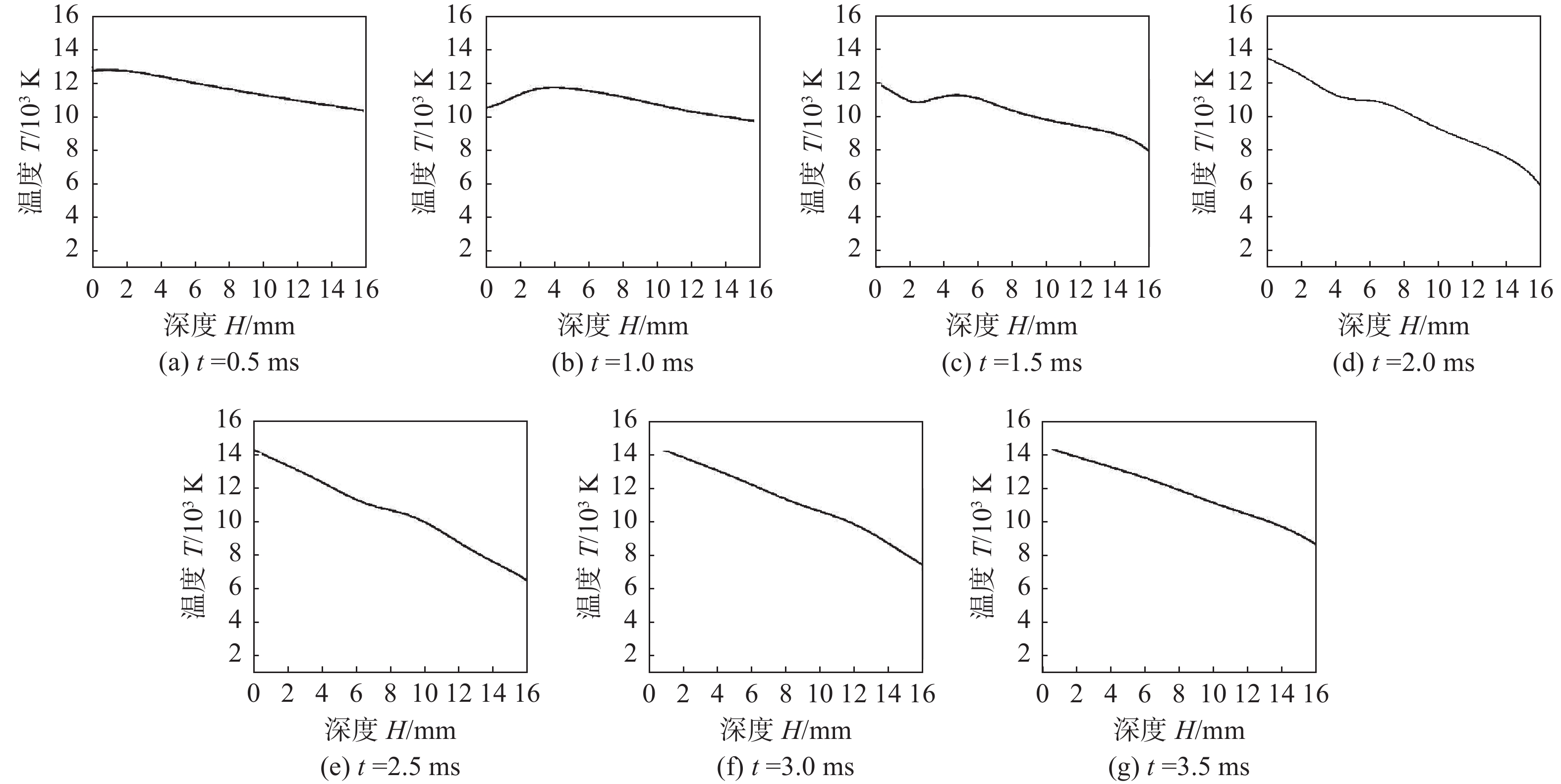
图6为5 mm厚铝合金焊接下EP时刻变极性等离子体电弧中心轴线温度分布。在EP阶段,可以看到由于电弧极性的改变,会使温度场有明显的扰动情况,该扰动的温度影响最大值为4 000 K。较之电弧稳定时的最高温度来看,那么各极性的扰动情况就是不可忽视的,持续时间越长会使熔池稳定性越低。在EP阶段,这种扰动的持续时间在2 ms内,占整个EP时长的50%。
图7为5 mm厚铝合金焊接下EN时刻变极性等离子体电弧中心轴线温度分布。在EN阶段,同样存在着电弧极性变化的情况,温度场有着明显的波动情况,温度扰动最大值为3 000 K。较之电弧稳定时的最高温度来看,那么各极性的扰动情况就是不可忽视的,持续时间越长会使熔池稳定性越低。而EN阶段扰动的持续时间也在2 ms内,占整个EN时长约为5%左右,持续稳定的热输入占整个焊接时长的84%。
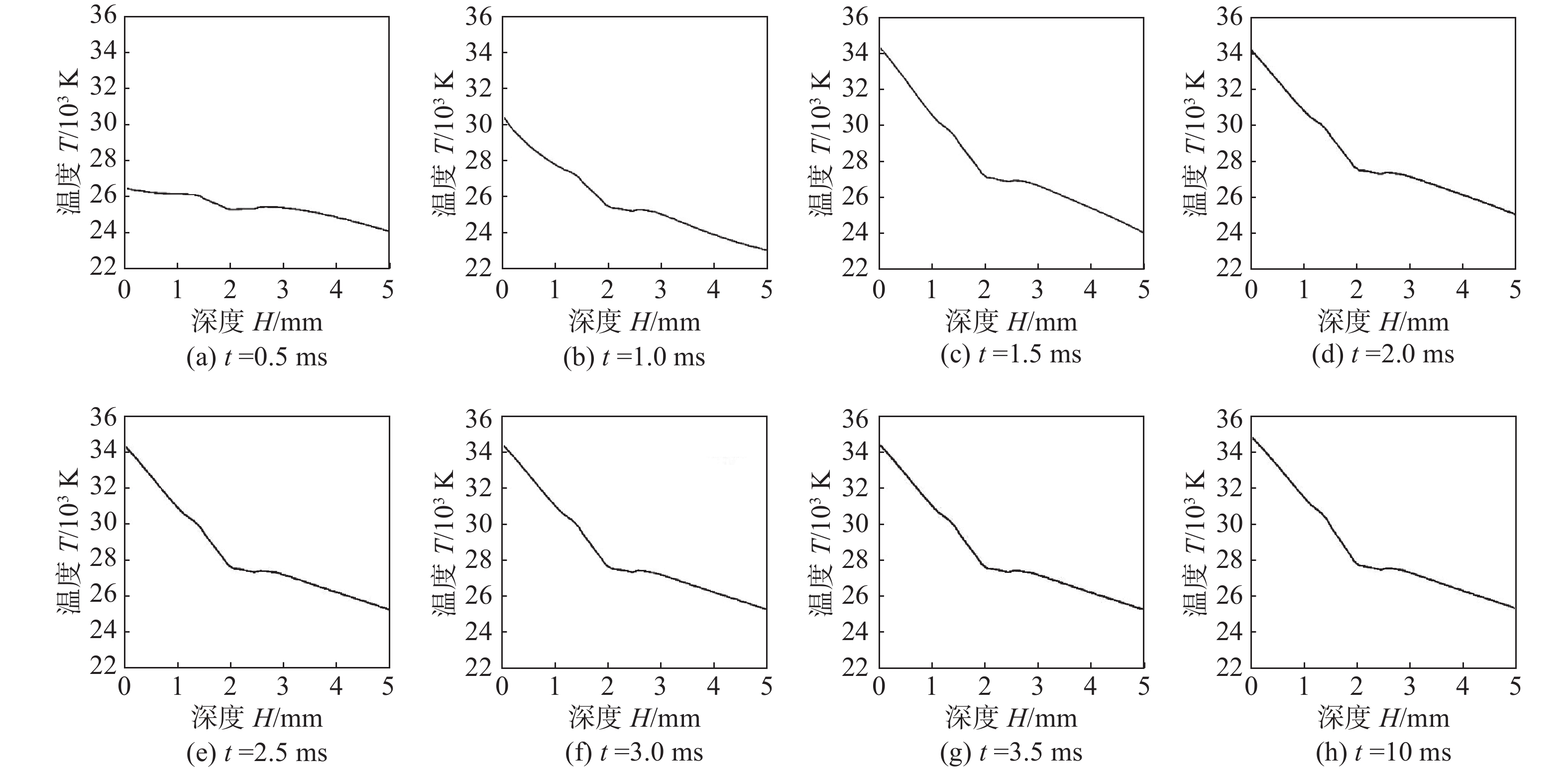
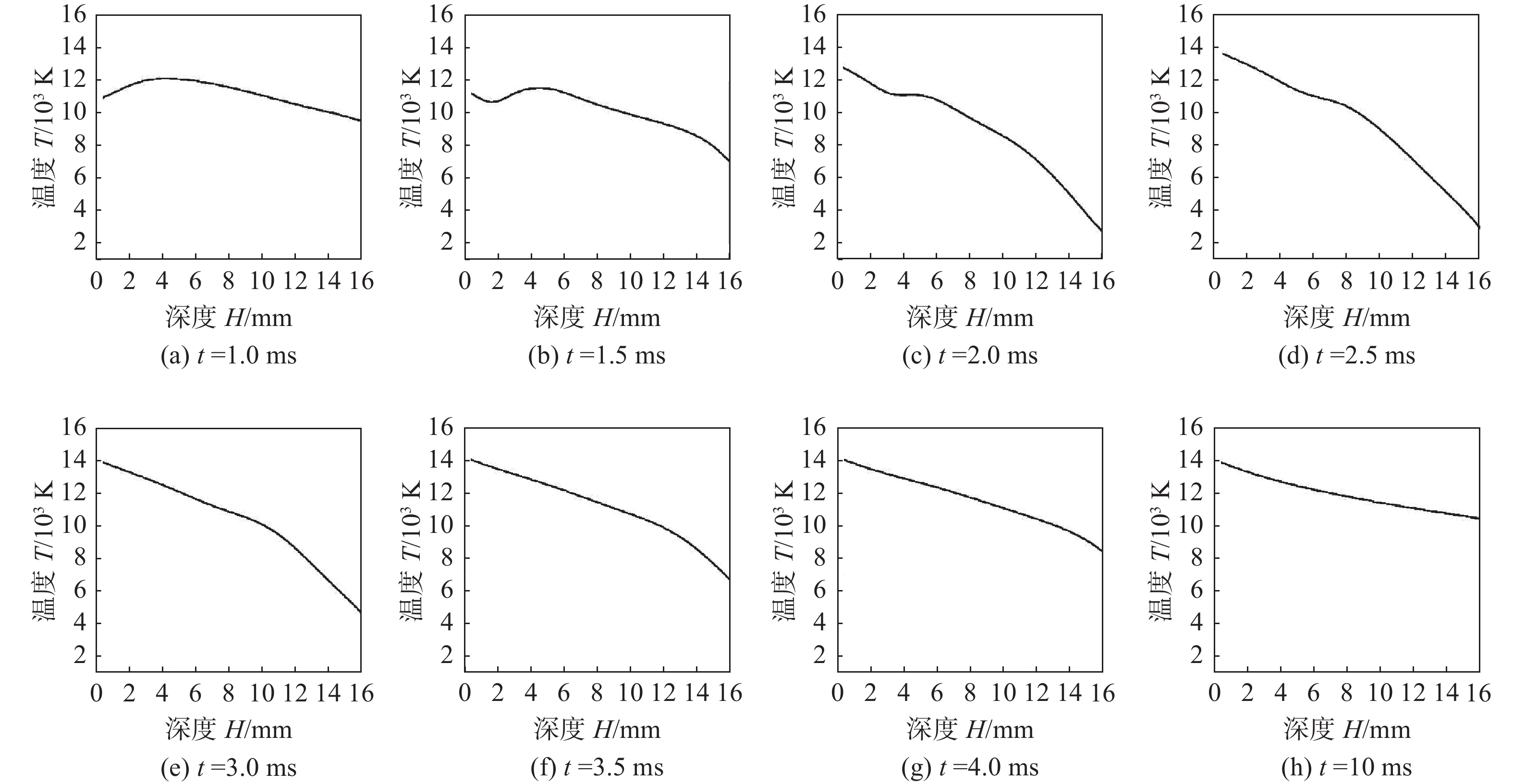
图8为16 mm厚铝合金焊接下EP时刻变极性等离子体电弧中心轴线温度分布。在EP阶段,由于电弧极性的改变,会使温度场有明显的扰动情况,该扰动的温度影响最大值为9 000 K。较之电弧稳定时的最高温度来看,各极性的扰动情况就是不可忽视的,持续时间越长会使熔池稳定性越低。EP阶段这种扰动的持续时间在2.5 ms内,占整个EP时长的62.5%。
图9为16 mm厚铝合金焊接下EN时刻变极性等离子体电弧中心轴线温度分布。在EN阶段,同样存在着电弧极性变化的情况,温度场有着明显的波动情况,温度扰动最大值为9 000 K。较之电弧稳定时的最高温度来看,各极性的扰动情况就是不可忽视的,持续时间越长会使熔池稳定性越低。EN阶段扰动的持续时间也在3 ms内,占整个EN时长约为14%左右,持续稳定的热输入占整个焊接时长的78%。电流是电弧热输入的最直接的影响因素,电流的增大会影响极性变化温度波动峰值的大小;但随着基板板厚的增加,失稳电弧回复时间会随之增加。回复时间的长短与温度波动峰值的大小对熔池热平衡有着重要的影响,回复时间越长。
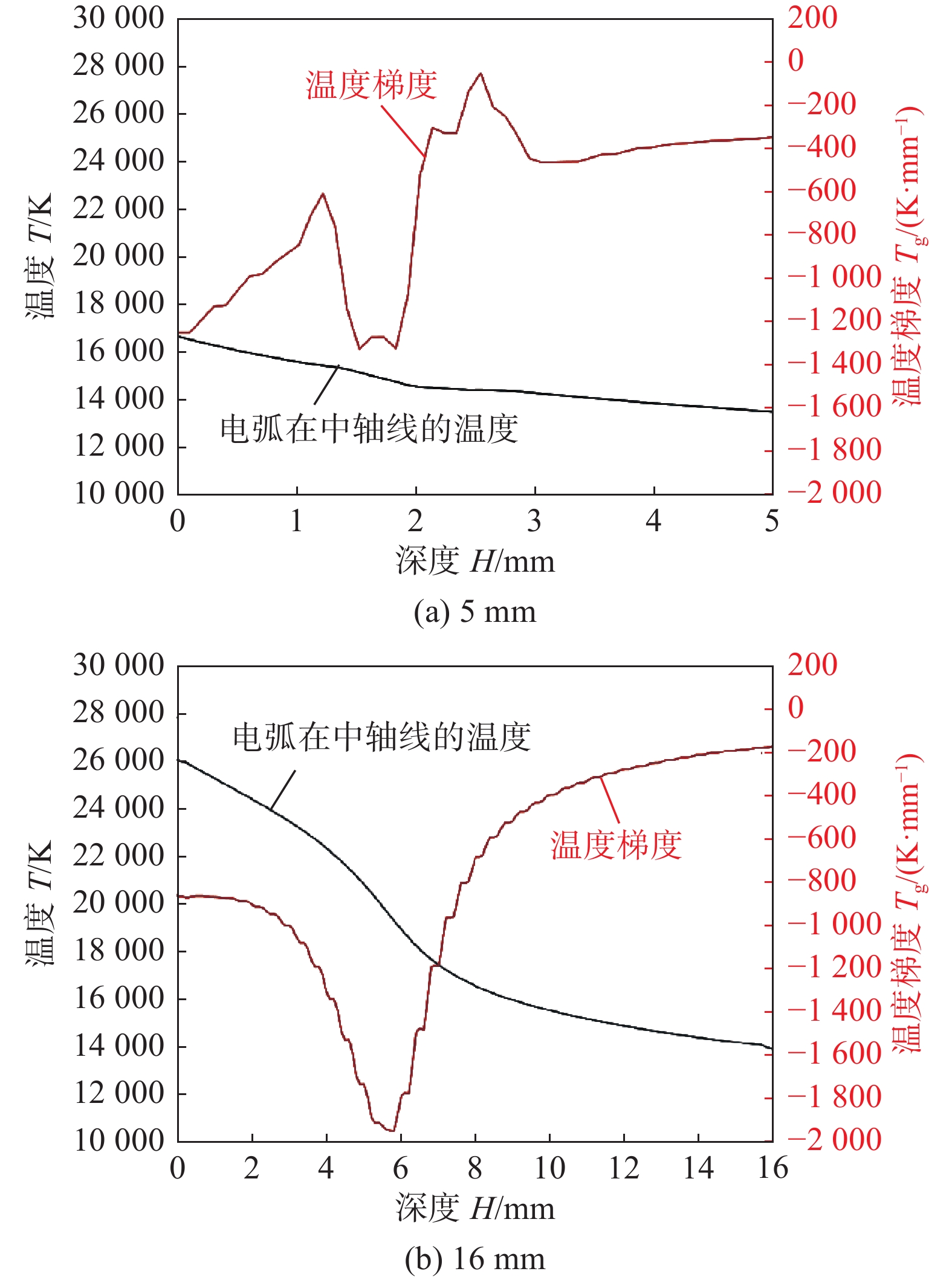
图10为不同板厚下变极性等离子电弧在中轴线的温度分布。图10a为变极性等离子弧焊焊接5 mm铝板材时,电弧位于小孔内部的中轴线上的温度分布及温度梯度变化情况。入口侧温度为16 500 K,出口侧温度为13 700 K;小孔内部温度呈一个持续衰减的趋势,且为线性温度衰减,温度梯度的最大峰值为1 400 K/mm,出现在深度为1.5 ~2.0 mm处。图10b为变极性等离子弧焊焊接16 mm铝板材时,电弧位于小孔内部的中轴线上的温度分布及温度梯度变化情况。入口侧温度为26 500 K,出口侧温度为13 700 K;小孔内部温度呈一个持续衰减的趋势,且为而二次温度衰减趋势,与线性衰减想比,衰减程度更大;温度梯度的最大峰值为2 000 K/mm,出现在深度为6 mm处。变极性等离子体焊接电弧在不同板厚的出口侧温度均为13 700 K左右,16 mm板厚的可能存在熔池稳定时电弧尾焰温度阈值。由于板厚的增加改变了温度分布的规律,5 mm板厚电弧温度的衰减情况为线性,使得熔池更容易稳定,而16 mm厚板焊接的电弧温度衰减情况为一个二次型,使得温度变化更加复杂,熔池稳定性较之前5 mm显然会降低很多。
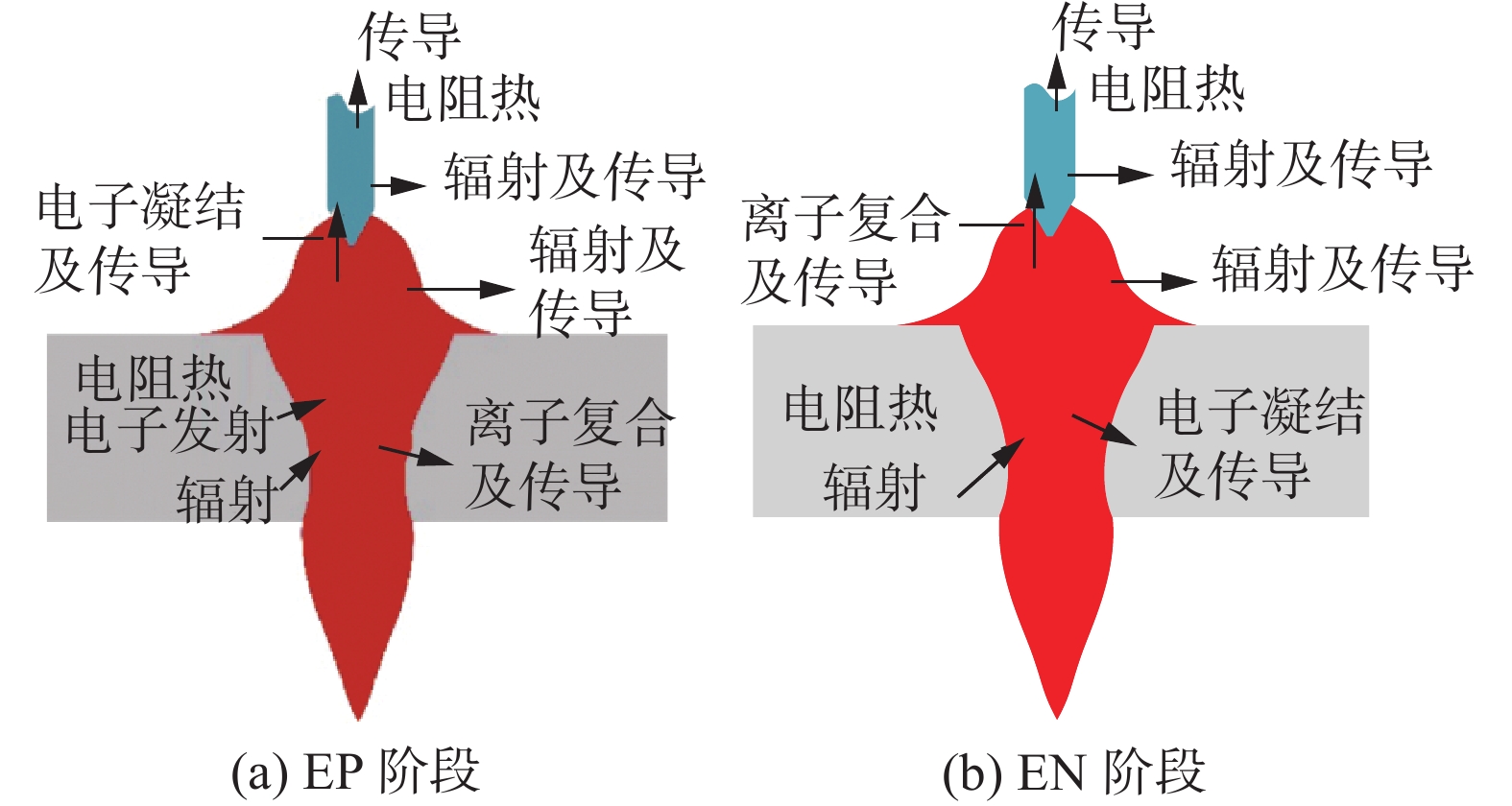
变极性等离子焊接过程是多物理场互相耦合的过程,试验变量繁多冗杂,其中所包含的能量传递也十分复杂。图11为变极性电弧在正反极性阶段能量平衡示意图。由上面电弧电流密度存在的差异,可以得到电弧在厚板焊接时能量衰减程度更大,电弧达到厚板底部已经消耗大部分能量,电弧本身处于临界平衡状态,在电弧极性转变的波动下更加熔池使熔池失稳。
3. 结论
(1)变极性等离子弧焊接5 mm厚度铝合金时,电流密度为1.0 × 106 A/m2以上的区域几乎涵盖整个小孔熔池,但是在焊接16 mm厚板铝合金时此电流密度为1.0 × 106 A/m2以上的区域仅达到深度为12 mm处,并没有覆盖作用在整个小孔,相应地也就没有5 mm熔池稳定性要高。
(2)电流的增大会影响极性变化温度波动峰值的大小;但随着基板板厚的增加,失稳电弧回复时间会随之增加。
(3)随着板厚的增加,变极性等离子弧温度分布发生改变,5 mm板厚电弧温度的衰减情况为线性,可能使得熔池更容易稳定,而16 mm厚板焊接的电弧温度衰减情况为二次型,使得温度变化更加复杂,较之前5 mm熔池稳定性或许会降低。
-
表 1 铝合金VPPA穿孔焊接工艺参数
板厚
b/mm离子气体流速
Q1/(L·min−1)保护气体流速
Q2/(L·min−1)EP电流
I/A交流频率
f/HzEN时间占比
η(%)弧高
h/mm钨极内缩
l/mm焊接速度
v/(mm·s−1)5 4.0 18.0 130~150 40 70 2.0 4.0 3.0 16 3.5 18.0 480~500 40 70 4.0 4.0 2.1 -
[1] 蒋凡. 穿孔等离子弧焊接电弧状态及熔池稳定性研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学博士学位论文, 2014. [2] 徐良, 吕晓春, 薛永, 等. 铝合金变极性等离子弧焊接的工况适应性[J]. 焊接, 2019(11):24 − 27. doi: 10.12073/j.hj.20190624005 [3] Irving B. Plasma arc welding takes on me advanced solid rocket motor[J]. Welding Journal, 1992, 71(12):49 − 50.
[4] Keanini R G, Rubinsky B. Plasma arc welding under normal and zero gravity[J]. Welding Journal, 1990, 69(6):41 − 50.
[5] 陈树君. 变极性等离子弧穿孔立焊工艺及装备[J]. 金属加工(热加工), 2013(s2):89 − 90. [6] 卢振洋, 余旭, 李方, 等. 基于STM32F407的全数字化等离子弧焊电源控制技术[J]. 焊接, 2019(4):16 − 22. doi: 10.12073/j.hj.20181220003 [7] 周阳, 齐铂金. VPPAW工艺的变极性焊接电流受控稳定性[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(4):16 − 25. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20211215003 [8] Zhang Y M, Zhang S B. Observation of the keyhole during plasma arc welding[J]. Welding Journal, 1999, 78(2):53 − 58.
[9] Short A B, McCartney D G, Webb P, et al. Influence of nozzle orifice diameter in keyhole plasma arc welding[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2011, 16(5):446 − 452. doi: 10.1179/1362171811Y.0000000013
[10] Shinoda K, Okubo M, Ito K, et al. The quality evaluation of advanced plasma welding technology[J]. Welding International, 2012, 26(7):511 − 515. doi: 10.1080/09507116.2011.590674
[11] 陈桂芳. 2A14铝合金VPPA横焊工艺及熔池行为研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学硕士学位论文, 2013. [12] 韩永全. VPPA特性及变断面铝合金穿孔等离子弧焊接工艺[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学博士学位论文, 2005. [13] 韩永全, 吕耀辉, 陈树君, 等. 变极性等离子电弧形态对电弧力的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2005, 26(5):49 − 52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2005.05.013 [14] 白雪宇. 厚板高强铝合金变极性等离子弧穿孔立焊熔池稳定性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学硕士学位论文, 2021. [15] 舒凤远. 厚板铝合金弧焊焊接接头组织及应力演变研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士学位论文, 2014. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 范佳兴,韩永全,张利国,孙振邦. 2A12铝合金Ar-He混合保护气VPPA焊接接头组织与力学性能. 焊接学报. 2025(01): 112-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 甘世明,张佳欣,包晓艳,韩永全,孙振邦. 能量配比对6 mm 7A52铝合金板材VPPA-MIG复合焊接残余应力分布的影响. 内蒙古工业大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(05): 461-466 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 蒋凡,张成钰,张国凯,徐斌,范成磊,陈树君. 铝合金变极性等离子弧焊接阴极斑点动态行为. 焊接. 2024(12): 1-11 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: