Microstructure and properties of submerged arc weld metal of 1 000 MPa grade high strength steel
-
摘要:
针对水电用1 000 MPa级高强钢设计了一种埋弧焊用焊丝、焊剂。借助JMat Pro软件对熔敷金属的组织和力学性能进行模拟,并通过拉伸试验、冲击试验、OM,SEM,EDS等手段对其进行评价。研究了熔敷金属成分和焊接热输入对熔敷金属组织及力学性能的影响。试验结果表明,研制的焊材焊接工艺性优良,通过控制合金元素含量使熔敷金属力学性能远高于标准值;重点分析了Cr含量对熔敷金属组织和力学性能的影响,熔敷金属中少量的Cr元素会提高针状铁素体含量,Cr元素含量较高时,会增加贝氏体含量,使熔敷金属强度不断提高,冲击韧性先提高后降低;随着焊接热输入的升高,熔敷金属中针状铁素体含量不断减少,先共析铁素体含量提高,组织粗化,熔敷金属强韧性不断降低。
-
关键词:
- 1 000 MPa级高强钢 /
- 熔敷金属 /
- 埋弧焊 /
- 大热输入
Abstract:Welding wire and welding flux were designed for submerged arc welding of 1000 MPa grade high strength steel used in hydropower. JMat Pro software was used to simulate microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal. Microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal were evaluated by means of tensile test, impact test, OM, SEM and EDS. Effects of weld metal composition and welding heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal were analyzed. The test results showed that the developed welding consumables had excellent welding process. Mechanical properties of weld metal were higher than standard values by controlling content of alloying elements. Effects of Cr content on microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal were particularly analyzed. A small amount of Cr in weld metal would increase needle ferrite content, while a higher Cr content would increase bainite content, which resulted in increasing strength and first increasing and then decreasing impact toughness of weld metal. As welding heat input increased, acicular ferrite content of weld metal decreased and pre-eutectic ferrite content increased, microstructure was coarsened, and strength and toughness of weld metal decreased.
-
0. 前言
水电作为一种清洁的可再生能源为中国社会经济发展、环境保护起到了重要作用[1]。在水电设施建设中,抽水蓄能水电站为电能调峰、调频、调相发挥了巨大作用[2]。近些年来,为了提高能源利用率抽水蓄能水电站不断向大容量高水头方向发展。其中,蜗壳和压力钢管作为抽水蓄能水电站的主要承压部件对于材料的强度、韧性和低裂纹敏感性要求随之不断提高,需要使用高强钢作为建造材料[3]。中国已经建成的乌东德、白鹤滩等水电站的蜗壳和压力钢管等设备大量使用了800 MPa级高强钢[4]。日本已将1 000 MPa级高强钢应用于神奈川水电站的设备建设中,采用更高强度的钢材大大提高了设备的稳定性,减少材料使用量,节约建设成本[5 − 6]。但目前中国暂无将1 000 MPa级高强钢应用于水电设施的实例。
为了建设更加优良的水电设施,中国宝钢研制了一种1 000 MPa级水电用钢,并完成了各种厚度的量产。但相应焊材的研发较少,熔敷金属高强韧性匹配和低裂纹倾向是焊材的研发难点。该文通过软件模拟、性能试验和组织观察设计了1 000 MPa级高强钢埋弧焊用焊丝和配套焊剂,并研究了主合金成分中Cr含量和焊接热输入对熔敷金属强韧性的影响。
1. 焊材制备与试验
1.1 焊材制备
考虑熔敷金属需要满足较高的强韧性匹配要求,设计焊丝成分中:P,S元素含量较低,减少熔敷金属中低熔点化合物,保证熔敷金属抗裂性较好;加入Cr,Ni元素促进形成针状铁素体,提高熔敷金属强韧性[7 − 8];通过Si,Mn元素控制熔敷金属中的O含量,同时Mn氧化物可以作为针状铁素体形核质点,提高熔敷金属韧性[9];加入Ti元素通过形成微合金氧化物促进形成针状铁素体,降低晶粒大小,提高熔敷金属强韧性[10]。熔敷金属含有一定C元素含量,保证熔敷金属强度;加入Mo元素减少金属化合物在晶界的偏聚,提高材料塑韧性。综上设计1 000 MPa级高强钢焊丝成分见表1。
表 1 1 000 MPa级高强钢焊丝成分(质量分数,%)C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo Ti Al Fe 0.05~0.15 0.15~0.30 1.5~2.5 ≤0.008 ≤0.005 0.4~0.8 2.0~3.5 0.5~1.0 0.01~0.03 0.01~0.03 余量 考虑1 000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属强韧性要求较高,因此设计氟碱型焊剂,控制熔敷金属中的P,S,O等元素。焊剂成分中CaF2可以改善熔敷金属流动性,使焊缝光滑美观,为除去氢的有害作用,加入适量CaF2以降低扩氢的含量[11];焊剂中加入SiO2可以提高熔敷金属的流动性,提高焊接时的电弧稳定性[12];MgO是碱性氧化物,通过改善合金液的碱性来控制熔敷金属中的杂质元素含量,提高熔敷金属脱渣效果[13];TiO2可以改善熔渣的粘度与界面张力,促进焊接过程中渣系的排出[14];Al2O3在焊剂成分中作为造渣剂,有利于熔渣的排出及后续的焊缝脱渣[15 − 16];CaO是一种碱性氧化物,对于熔渣的酸碱度有调控作用,同时CaO具有排S,P作用[17];通过硅锰合金联合脱氧,降低熔敷金属中的氧化物含量,保证熔敷金属强韧性较高。设计焊剂成分见表2。
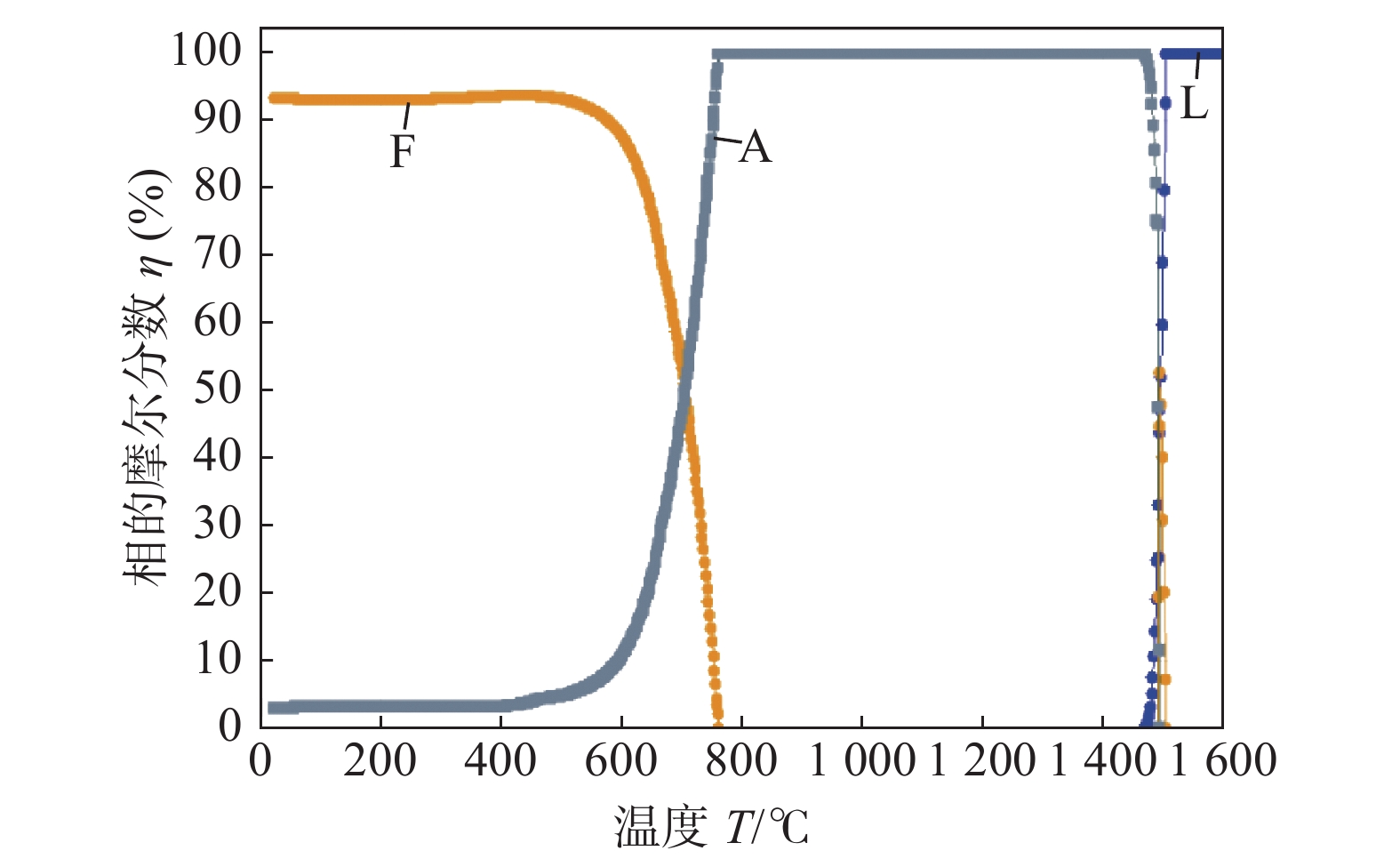
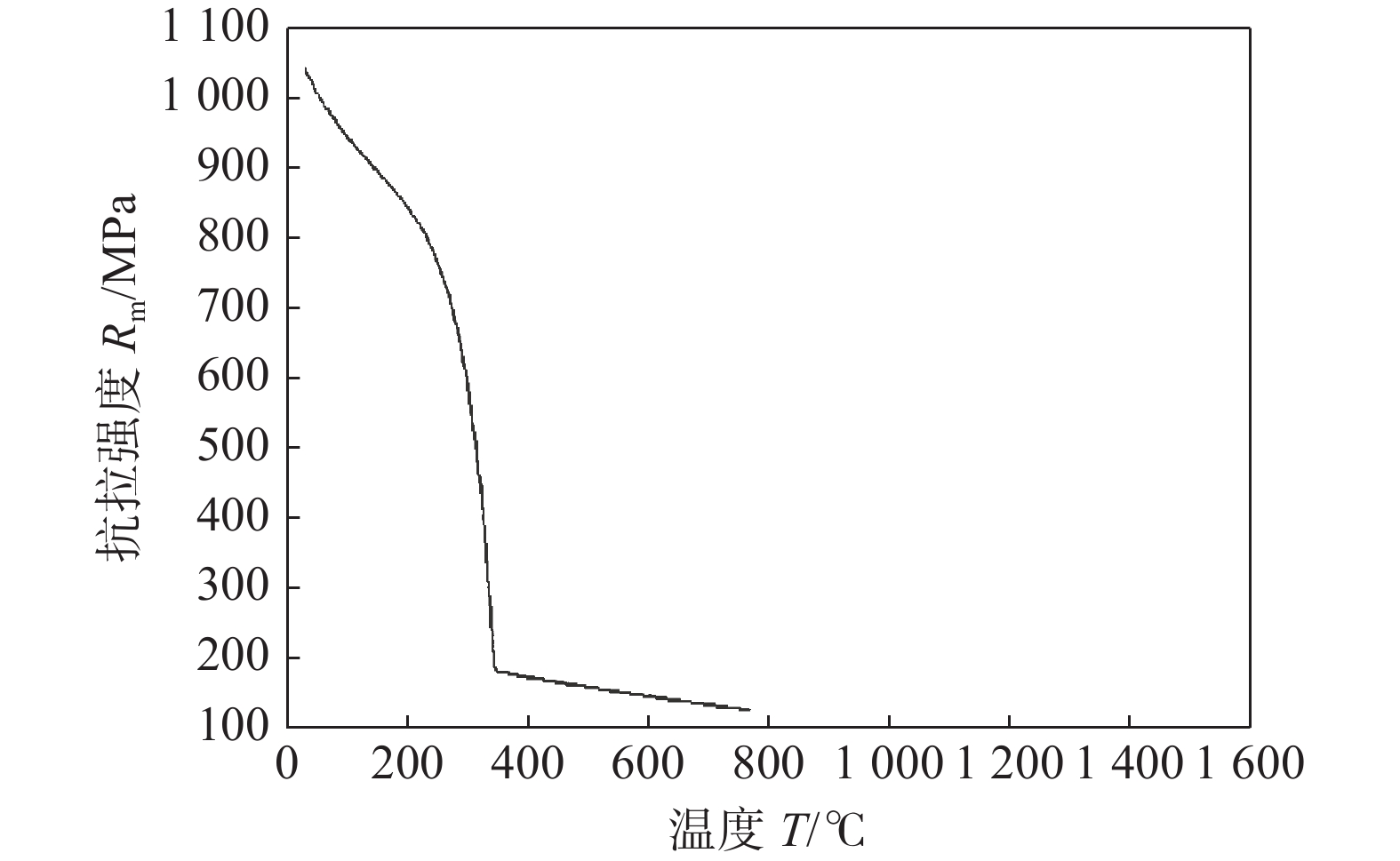
表 2 1 000 MPa级高强钢焊剂成分(质量分数,%)CaF2 SiO2 MgO TiO2 Al2O3 CaO 硅锰铁合金 20~28 5~8 18~21 5~8 16~24 16~22 1.0~4.5 采用JMat Pro7.0软件对1 000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属的组织和性能进行模拟,在组织模拟中,材料种类选择“General Steel”,输入熔敷金属成分后,选择“Step Temperature”;起始温度设置为1 600 ℃,结束温度设置为25 ℃,步长设置为2 ℃。在力学性能模拟中,输入熔敷金属成分后,选择“phases and properties”,晶粒度选择ASTM标准设置为9级,起始温度设置为1 600 ℃,冷却速度设置为50 ℃/s,计算熔敷金属抗拉强度。熔敷金属组织及力学性能模拟结果分别如图1和图2所示。由组织和力学性能模拟结果可知,设计的焊材成分制得熔敷金属抗拉强度高于标准值,熔敷金属组织模拟结果以铁素体(F)为主,含有少量奥氏体(A),高强钢熔敷金属设计思路为通过调控熔敷金属中的针状铁素体含量来提高熔敷金属强韧性,熔敷金属组织模拟结果表明设计的焊材成分符合要求。
1.2 试验过程
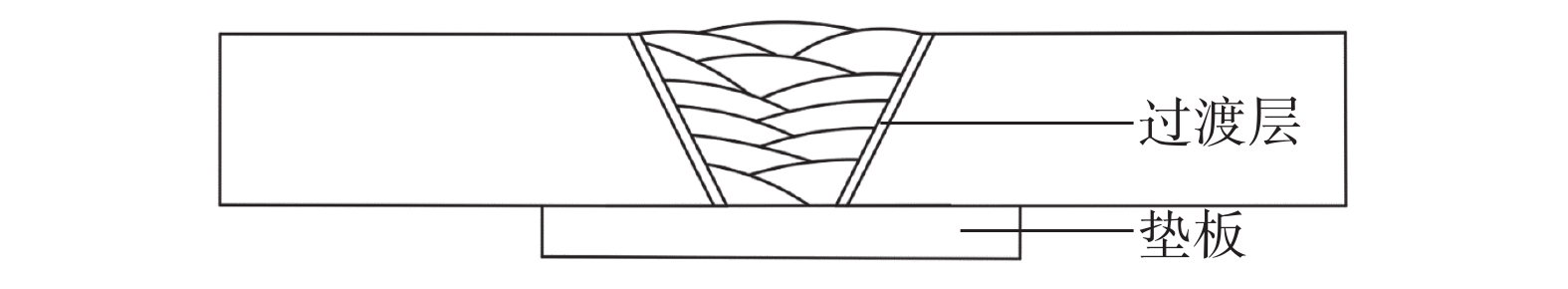
选用16Mn板材,板材尺寸为300 mm×300 mm×20 mm,开45° V形坡口,试板底部间隙为20 mm,试板底部放置300 mm×30 mm×10 mm垫板,采用哈尔滨威尔公司生产的1 000 MPa级高强钢焊条J107G,在坡口表面堆焊3 mm过渡层,焊接试板示意图如图3所示。采用研制的1 000 MPa级高强钢埋弧焊材焊接试板,焊丝直径为ϕ3.2 mm,焊接工艺参数见表3。
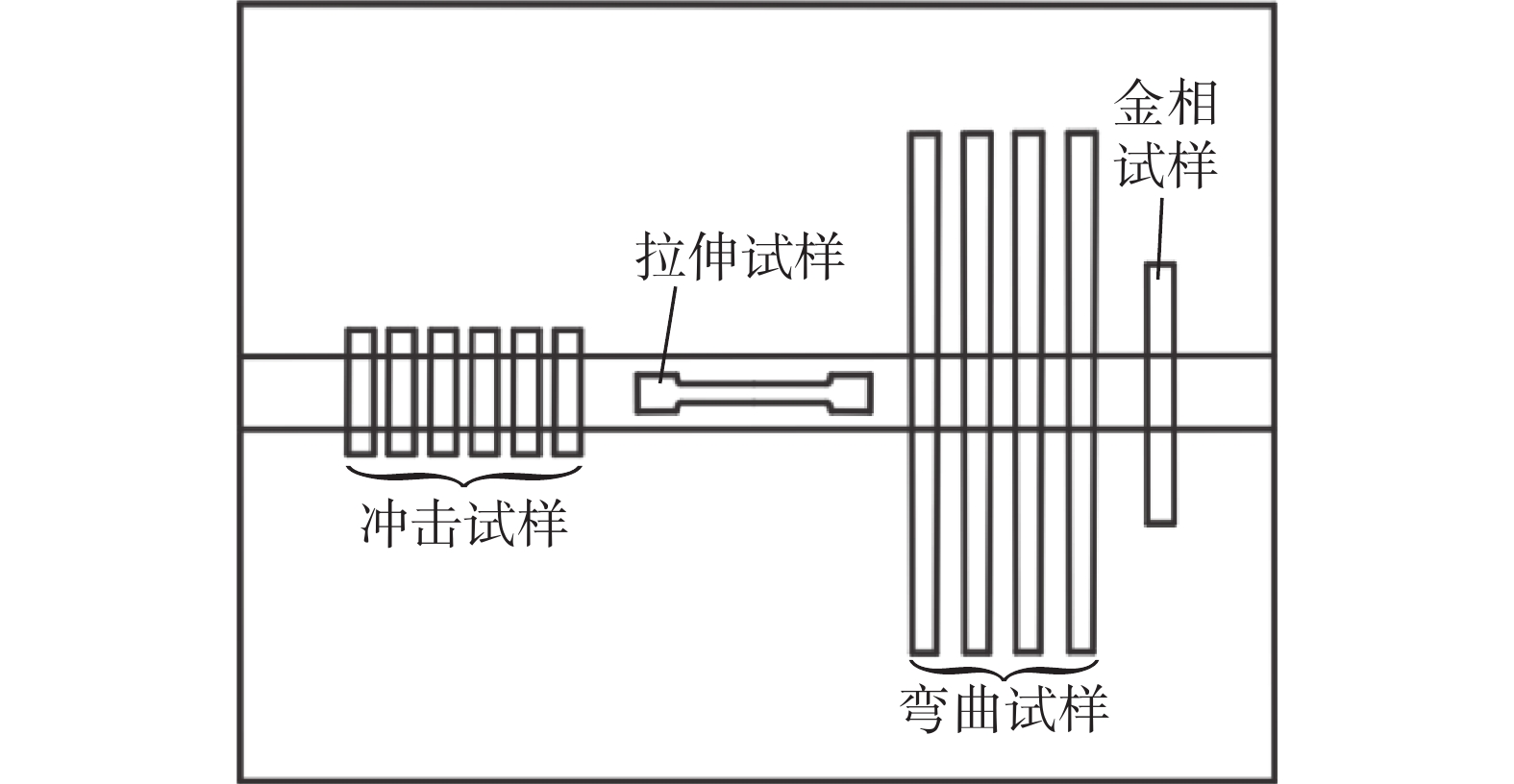
表 3 焊接工艺参数焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接速度v/(cm·min−1) 450 32 40 层间温度T0/℃ 后热温度T1/℃ 焊接热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) $\leqslant $150 350 21.6 焊接试板两侧起弧和收弧处由于电弧不稳定常存在熔敷金属成分不均匀的问题,因此焊道两侧各去头10 mm。依据GB/T 228.1《金属材料 拉伸试验 第1部分:室温试验方法》标准制备1个拉伸试样,在UTM5305SYXL电子拉伸试验机上进行拉伸试验;依据GB/T 229《金属材料 夏比摆锤冲击试验方法》标准制备用于−40 ℃和−60 ℃冲击试样各3个,在JBN-300B冲击试验机上进行夏比V形缺口冲击试验;依据GB/T 232《金属材料 弯曲试验方法》标准制备4个弯曲试件,在WAW-300万能试验机上进行弯曲试验;取样示意图如图4所示。
在熔敷金属中间部位取样制备金相试样,用4%的硝酸酒精溶液进行化学浸蚀,通过OLYMPUSGX51型光学显微镜观察熔敷金属的金相组织,利用ZEISS EVO18型扫描电子显微镜观察−40 ℃低温冲击试样断口熔敷金属微观组织形貌。
2. 熔敷金属组织及力学性能
2.1 焊接工艺性及力学性能
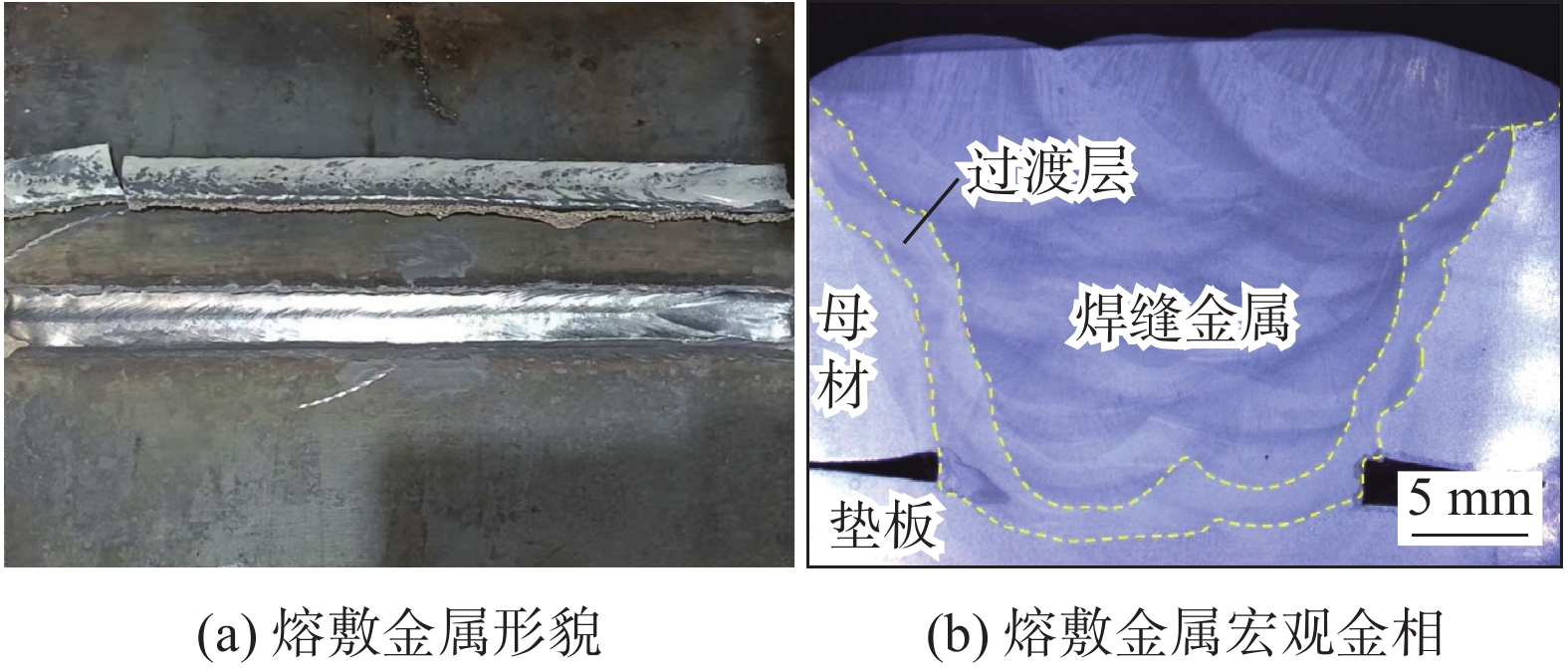
熔敷金属形貌和熔敷金属宏观金相如图5所示。设计的焊材工艺性优良,焊接过程中无飞溅,渣壳脱渣效果好,熔敷金属平直光滑,没有咬边、夹渣、凹坑等情况。宏观金相中无裂纹,无未焊透区域,熔敷金属为典型的柱状晶形貌。项目对1 000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属力学性能要求及熔敷金属力学性能试验值见表4,熔敷金属力学性能实测值均高于项目对熔敷金属力学性能要求且留有较大裕量,实际熔敷金属抗拉强度试验数据与JMat Pro模拟结果相近。
表 4 熔敷金属力学性能类别 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度RP0.2/MPa 断后伸长率A(%) −60℃冲击吸收能量AKV1/J −40℃冲击吸收能量AKV2/J 要求值 $\geqslant $950 $\geqslant $820 $\geqslant $14 $\geqslant $47 $\geqslant $52 实测值 976 851 18 60,65,63 88,86,92 2.2 熔敷金属组织
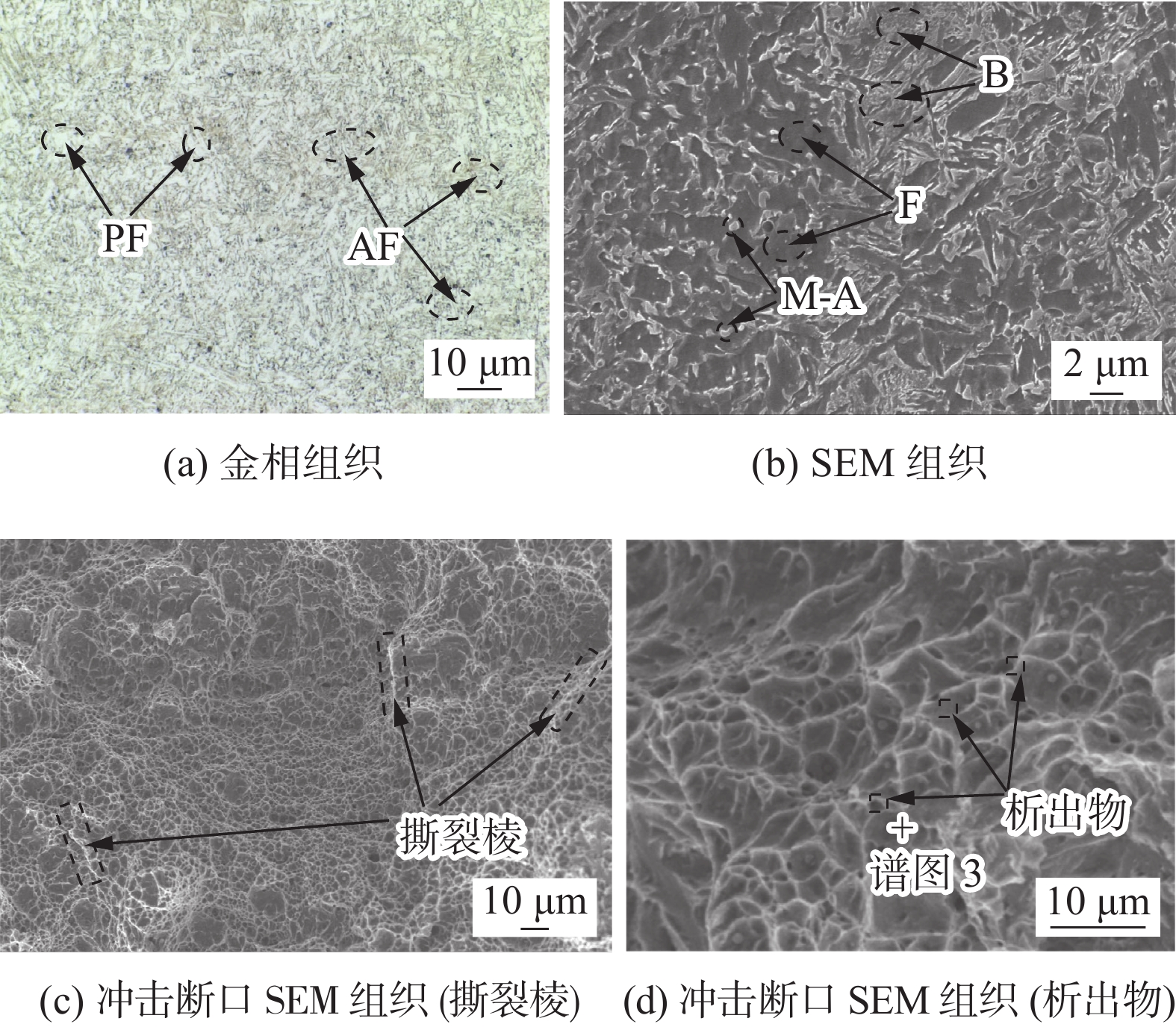
熔敷金属组织如图6所示,由图6a、图6b可知熔敷金属组织包括铁素体(F)、贝氏体(B)和M-A组元。铁素体以针状铁素体(AF)为主,针状铁素体尺寸较小,分布细密,为熔敷金属提供良好的强韧性,此外熔敷金属中还含有一部分先共析铁素体(PF)。M-A组元强度较高,熔敷金属中均匀分布的细小M-A组元对位错滑移具有阻碍作用,可以提高熔敷金属的强韧性。但熔敷金属中M-A组元较多时,会发生偏聚,成为裂纹的启裂源,严重影响熔敷金属的强韧性。图6b中以粒状在熔敷金属表面均匀分布的M-A组元,是熔敷金属保证较高强韧性的重要原因。对比发现熔敷金属组织和性能试验结果与JMat Pro模拟结果相似,通过模拟软件计算的性能和组织具有一定的准确性,因此可以考虑使用JMat Pro软件辅助1 000 MPa级高强钢焊丝成分设计。熔敷金属冲击断口为细小的韧窝形貌如图6c、图6d所示,韧窝中央含有较小的析出物,断裂方式为微孔聚集导致的韧性断裂,证明设计焊材制得的熔敷金属具有较高的强韧性。通过EDS对图6d所示的析出物进行分析,析出物成分包括Ti,Cr,Mn,Fe等元素。Ti,Cr,Mn形成的化合物作为形核质点,促进熔敷金属形成针状铁素体,提高熔敷金属强韧性,析出物成分见表5。
表 5 析出物成分(质量分数,%)Ti Cr Mn Fe 0.75 0.76 11.08 87.42 3. 成分优化
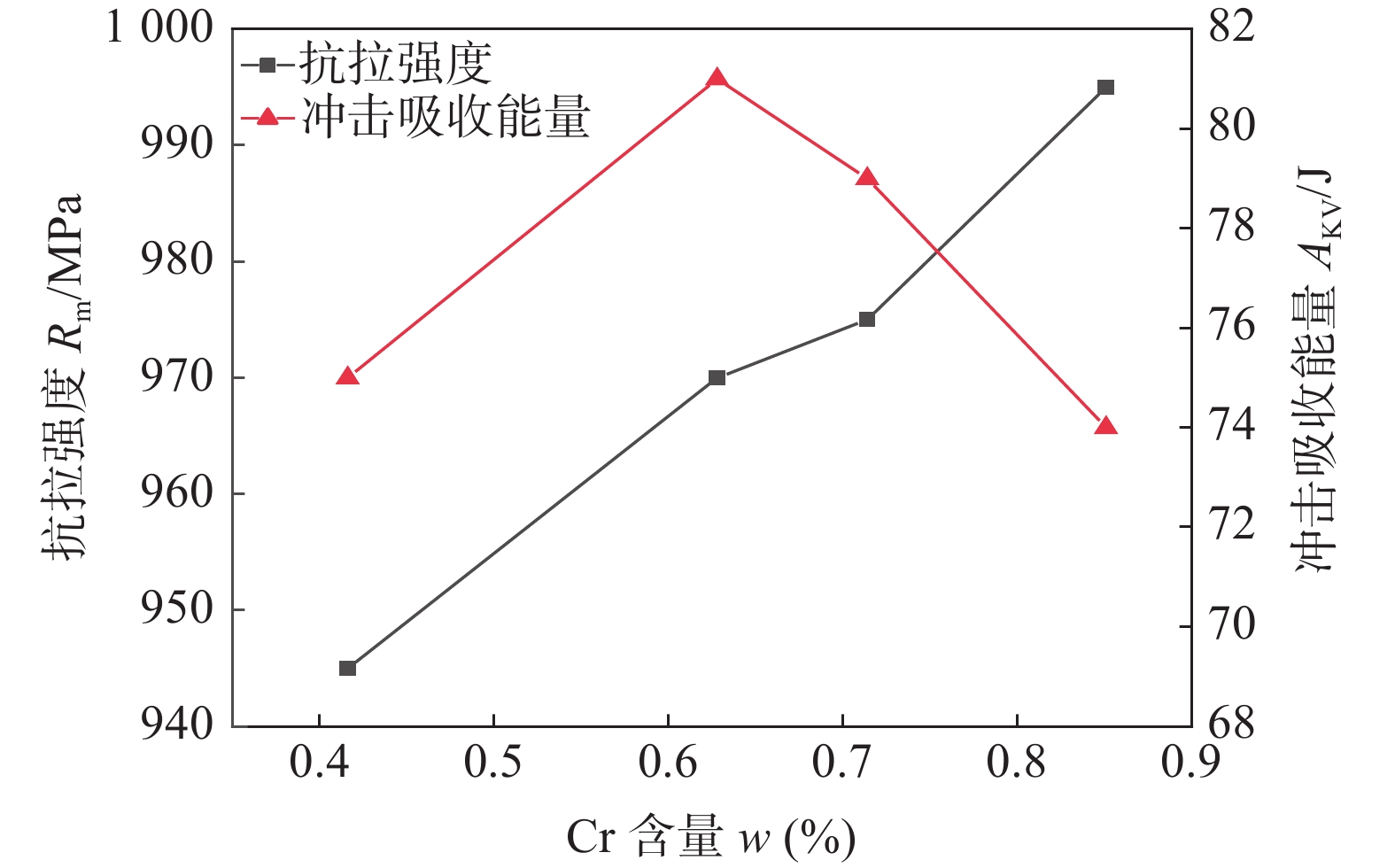
对1 000 MPa级高强钢埋弧焊丝设计,学者提出了Cr含量为0%~0.5%的低Cr焊丝和Cr含量为0.5%~1.2%的高Cr焊丝2种思路,该文在保持其他成分不变的情况下,研究了Cr含量变化对熔敷金属组织性能的影响,确定熔敷金属中Cr含量的最佳值。通过在焊剂中加入Cr铁粉向熔敷金属中过渡Cr,采用表3焊接工艺参数对试板进行焊接,得到熔敷金属中的Cr含量分别为0.416%,0.628%,0.714%,0.851%,熔敷金属力学性能见表6,熔敷金属强韧性匹配关系如图7所示。
表 6 不同Cr含量熔敷金属力学性能编号 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度Rp0.2/MPa 断后伸长率A(%) −40 ℃冲击吸收能量AKV2/J 侧向弯曲试验(D=4a,α=180°) 1 945 860 16.0 72,76,77 无裂纹 2 970 875 19.0 82,83,78 无裂纹 3 975 880 16.5 77,78,82 无裂纹 4 995 935 17.5 72,73,77 无裂纹 标准值 $\geqslant $950 $\geqslant $820 $\geqslant $14 $\geqslant $47 实测 试验结果表明:随着Cr含量增加,熔敷金属抗拉强度提高,而熔敷金属冲击韧性随着Cr含量增加,先提高后降低。即Cr含量在一定量时可以保证较好的强韧性匹配。
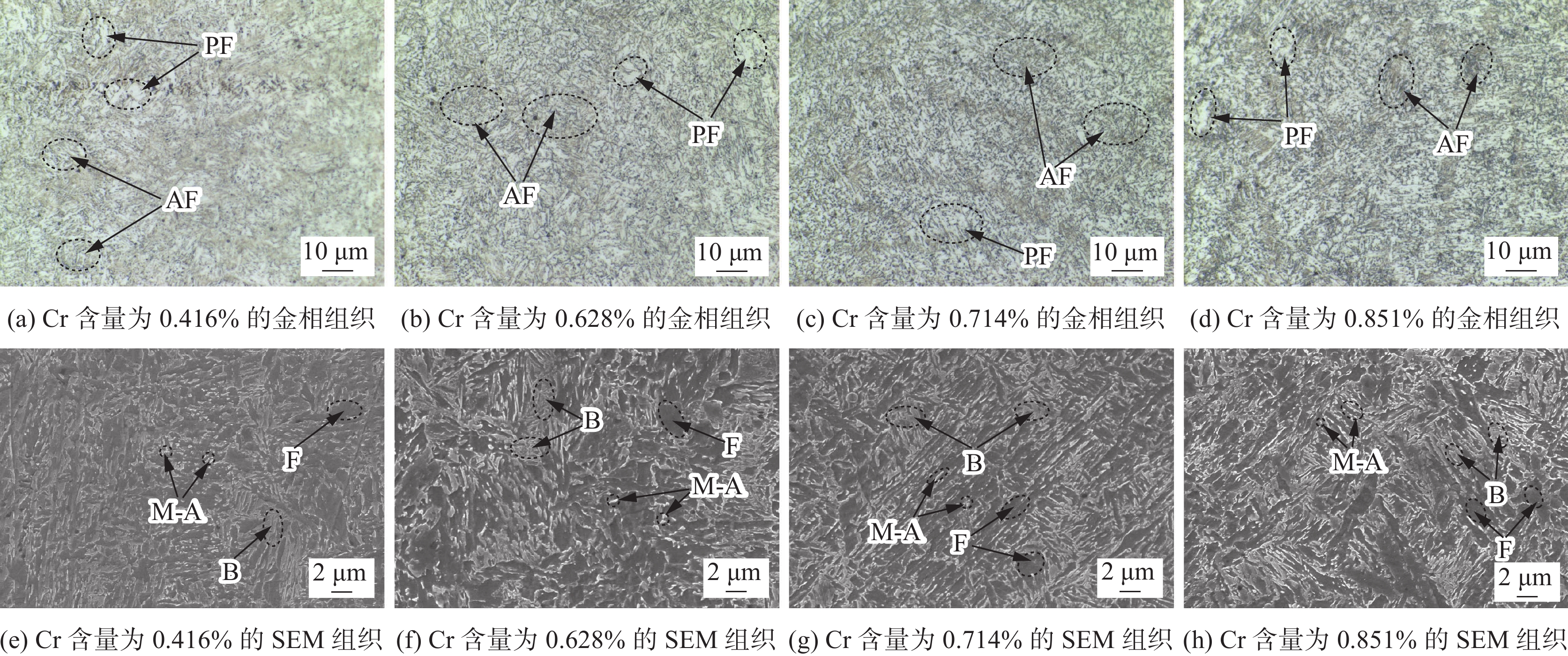
图8为不同Cr含量熔敷金属组织。在熔敷金属金相组织中,随着Cr含量增加,针状铁素体含量提高,先共析铁素体含量减少。针状铁素体呈小角度晶界,有利于降低熔敷金属的缺口敏感性,阻碍裂纹扩展,因此针状铁素体增加可以提高熔敷金属强韧性。而先共析铁素体是多边形为大角度晶界,对于裂纹的阻碍作用较弱,所以含有一定量的Cr有利于提高熔敷金属的强韧性。但随着Cr含量进一步提高,贝氏体和M-A组元含量提高,M-A组元是强硬相;当Cr含量较低时,熔敷金属中M-A组元分布均匀,通过阻碍位错运动提高熔敷金属强韧性;但随着Cr含量提高,熔敷金属中M-A组元以细条状偏聚使熔敷金属应力集中,降低材料强韧性。因此,随着Cr含量的增加,熔敷金属的强度提高,而韧性会表现出先升高后降低的趋势,为保证焊丝较好的强韧性匹配效果确定焊丝成分中的Cr含量为0.6%。
4. 大热输入焊接试验
大容量高水头水电设备所用钢材厚度较大,需要采用大热输入焊接来提高熔深和焊接效率,但大热输入焊接也带来了合金元素烧损,熔敷金属晶粒粗大等问题,因此该文研究了设计的焊材在大热输入下焊接的熔敷金属组织与性能。在焊材成分中,由Cr含量对熔敷金属强韧性的影响试验,添加Cr含量至0.6%,保持焊材其他成分不变,焊接工艺参数和熔敷金属力学性能分别见表7、表8。随着焊接热输入的提高,熔敷金属强度先提高后降低,冲击韧性不断降低。
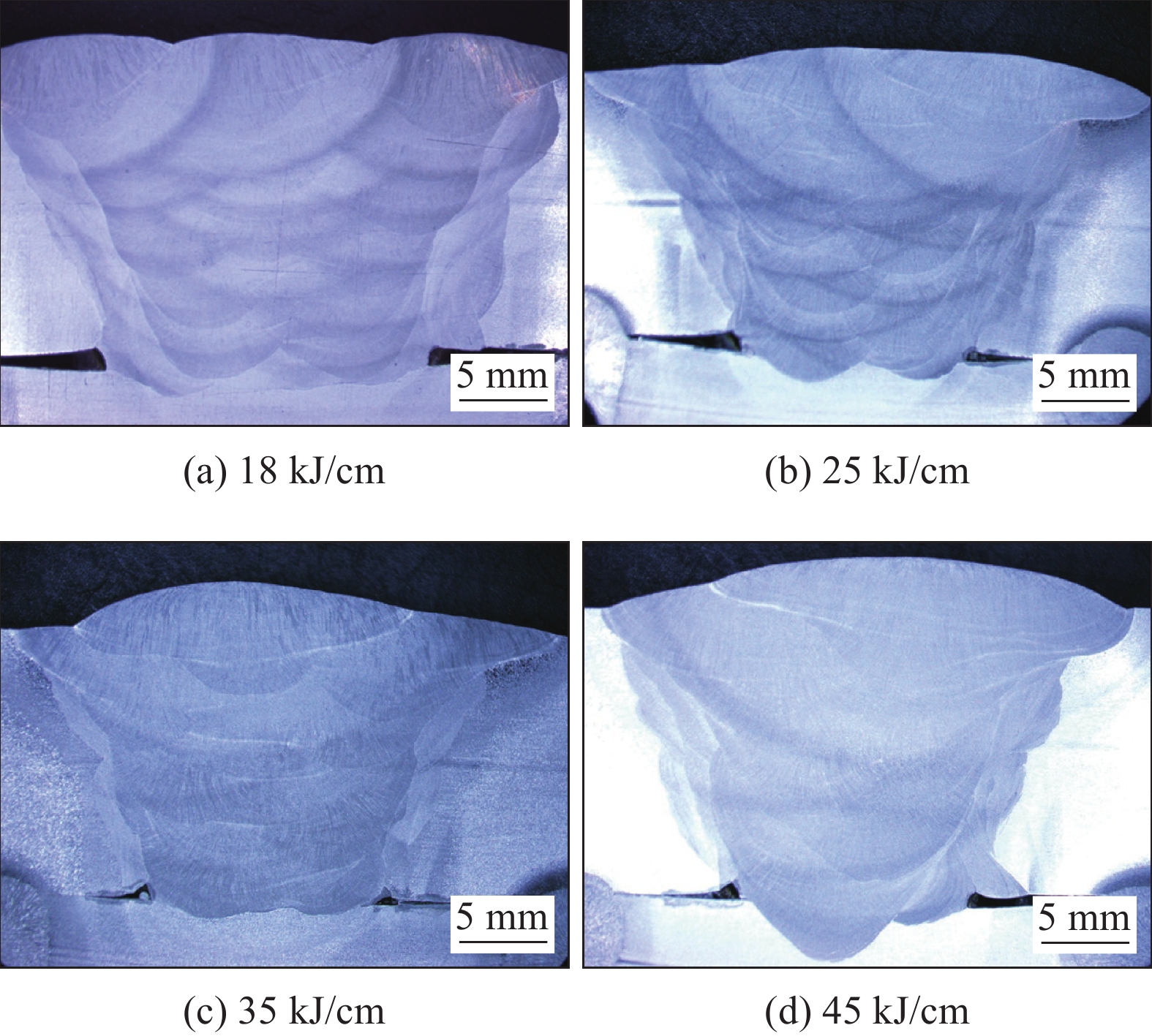
表 7 焊接热输入参数设置焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接速度v/(cm·min−1) 焊接热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 层间温度T0/℃ 后热温度T1/℃ 450 30 45 18 $\leqslant $150 350 500 32 38 25 $\leqslant $150 350 500 32 27 35 $\leqslant $150 350 550 34 25 45 $\leqslant $150 350 表 8 熔敷金属力学性能编号 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度RP0.2/MPa 断后伸长率A(%) −40 ℃冲击吸收能量AKV2/J 侧向弯曲试验(D=4a,α=180°) 1 975 870 18.0 84,80,85 无裂纹 2 980 885 18.0 75,77,71 无裂纹 3 910 805 14.5 60,55,59 无裂纹 4 855 745 14.0 49,51,45 无裂纹 标准值 $\geqslant $950 $\geqslant $820 $\geqslant $14 $\geqslant $47 实测 单道堆焊形貌和和宏观金相分别如图9、图10所示。热输入由低到高熔敷金属的熔宽分别为15 mm,20 mm,22.5 mm,31 mm,熔深分别为4.5 mm,5.5 mm,6.5 mm,7 mm。随着焊接热输入增加,焊接道数依次为14道、10道、7道和6道,焊接效率提高明显。由宏观金相可知随着热输入提高焊道间受高温热循环区域扩大,多次高温热循环使熔敷金属晶粒异常长大,降低熔敷金属强韧性。
不同热输入熔敷金属金相组织如图11所示,图11a为焊接热输入18 kJ/cm时的熔敷金属组织,以针状铁素体为主,含有少量先共析铁素体和M-A组元。图11b为焊接热输入25 kJ/cm时的熔敷金属组织,以准多边形铁素体(QF)为主、先共析铁素体含量较少。准多边形铁素体晶粒细小,熔敷金属强韧性较好。图11c为焊接热输入35 kJ/cm时的熔敷金属组织,先共析铁素体含量增加,熔敷金属力学性能进一步降低。图11d为焊接热输入45 kJ/cm时的熔敷金属组织,为粗大的先共析铁素体、同时M-A组元含量增加,熔敷金属强度和韧性均有较大下降。
5. 结论
(1)研制了一种1 000 MPa级高强钢埋弧焊用焊材,经试验其焊接工艺性优良,力学性能远高于标准要求,满足1 000 MPa级高强钢埋弧焊工程应用指标要求。
(2)熔敷金属中少量的Cr元素会提高针状铁素体含量,Cr含量较高时,会增加贝氏体含量,因此随着熔敷金属中Cr含量提高,强度不断提高,冲击韧性先升高后降低,通过试验确定熔敷金属中Cr含量为0.6%时强韧性匹配效果最好。
(3)随着焊接热输入提高,熔敷金属中针状铁素体含量不断减少,先共析铁素体含量提高,熔敷金属组织粗化,强韧性降低,实际使用需要控制热输入。
-
表 1 1 000 MPa级高强钢焊丝成分(质量分数,%)
C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo Ti Al Fe 0.05~0.15 0.15~0.30 1.5~2.5 ≤0.008 ≤0.005 0.4~0.8 2.0~3.5 0.5~1.0 0.01~0.03 0.01~0.03 余量 表 2 1 000 MPa级高强钢焊剂成分(质量分数,%)
CaF2 SiO2 MgO TiO2 Al2O3 CaO 硅锰铁合金 20~28 5~8 18~21 5~8 16~24 16~22 1.0~4.5 表 3 焊接工艺参数
焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接速度v/(cm·min−1) 450 32 40 层间温度T0/℃ 后热温度T1/℃ 焊接热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) $\leqslant $150 350 21.6 表 4 熔敷金属力学性能
类别 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度RP0.2/MPa 断后伸长率A(%) −60℃冲击吸收能量AKV1/J −40℃冲击吸收能量AKV2/J 要求值 $\geqslant $950 $\geqslant $820 $\geqslant $14 $\geqslant $47 $\geqslant $52 实测值 976 851 18 60,65,63 88,86,92 表 5 析出物成分(质量分数,%)
Ti Cr Mn Fe 0.75 0.76 11.08 87.42 表 6 不同Cr含量熔敷金属力学性能
编号 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度Rp0.2/MPa 断后伸长率A(%) −40 ℃冲击吸收能量AKV2/J 侧向弯曲试验(D=4a,α=180°) 1 945 860 16.0 72,76,77 无裂纹 2 970 875 19.0 82,83,78 无裂纹 3 975 880 16.5 77,78,82 无裂纹 4 995 935 17.5 72,73,77 无裂纹 标准值 $\geqslant $950 $\geqslant $820 $\geqslant $14 $\geqslant $47 实测 表 7 焊接热输入参数设置
焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接速度v/(cm·min−1) 焊接热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 层间温度T0/℃ 后热温度T1/℃ 450 30 45 18 $\leqslant $150 350 500 32 38 25 $\leqslant $150 350 500 32 27 35 $\leqslant $150 350 550 34 25 45 $\leqslant $150 350 表 8 熔敷金属力学性能
编号 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度RP0.2/MPa 断后伸长率A(%) −40 ℃冲击吸收能量AKV2/J 侧向弯曲试验(D=4a,α=180°) 1 975 870 18.0 84,80,85 无裂纹 2 980 885 18.0 75,77,71 无裂纹 3 910 805 14.5 60,55,59 无裂纹 4 855 745 14.0 49,51,45 无裂纹 标准值 $\geqslant $950 $\geqslant $820 $\geqslant $14 $\geqslant $47 实测 -
[1] Li Xiaozhu, Chen Zhijun, Fan Xiaochao, et al. Hydropower development situation and prospects in China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 82: 232 − 239. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.090
[2] Pérez-Díaz J I, Chazarra M, García-González J, et al. Trends and challenges in the operation of pumped-storage hydropower plants[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 44: 767 − 784. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.01.029
[3] 冯路路, 吴开明, 余宏伟, 等. 高强韧水电站用钢的生产现状及发展趋势[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2020, 32(3): 175 − 185. [4] 程惠, 赵爽, 宋建军. 800 MPa高强钢在白鹤滩右岸压力钢管工程中的应用[J]. 水电与新能源, 2017(7): 1 − 7. [5] Horikawa K, Watanabe N. Application of extra-high tensile strength steel for hydropower plants in japan [C]//Conference on High Strength Steels for Hydropower Plants, Takasaki, Japan, 2005: 1 − 8.
[6] Hara N, Sato M. Development and application of welding consumables for 950 MPa class high strength steels [C]//Conference on High Strength Steels for Hydropower Plants, Takasaki, Japan, 2009.
[7] 刘政军, 裘荣鹏, 武丹, 等. 960 MPa高强钢金属粉芯型药芯焊丝焊缝金属韧化机理[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(1): 102 − 106. [8] 张敏, 张林, 王博玉, 等. 药芯焊丝镍含量对25Cr2Ni4MoV高强钢焊接接头组织与性能的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2022, 46(12): 67 − 71. [9] Jiang Q L, Li Y J, Wang J , et al. Effects of inclusions on formation of acicular ferrite and propagation of crack in high strength low alloy steel weld metal [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2011, 27(10): 1565 − 1569.
[10] Jiang Q L, Li Y J, Wang J, et al. Effects of Mn and Ti on microstructure and inclusions in weld metal of high strength low alloy steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2011, 27(9): 1385 − 1390. doi: 10.1179/026708310X12701149768052
[11] 张敏, 姚成武, 李继红, 等. X80管线钢埋弧焊用烧结焊剂的研制[J]. 焊接学报, 2006, 27(10): 29 − 32. [12] Sharma L, Chhibber R. Investigating the physicochemical and thermophysical properties of submerged arc welding fluxes designed using TiO2-SiO2-MgO and SiO2-MgO-Al2O3 flux systems for linepipe steels[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(2): 1569 − 1587. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.032
[13] 丁光柱, 郭未昀, 王顺兴, 等. 氧化镁对不锈钢埋弧焊剂SJ601抗潮性和脱渣性影响[J]. 焊接技术, 2020, 49(5): 90 − 93. [14] 何磊, 王任甫, 成应晋, 等. TiO2和Al2O3对CaO-SiO2-CaF2基础焊接渣系熔化特性的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(5): 7 − 13, 61. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220616003 [15] Sharma L, Chhibber R. Design & development of SAW fluxes using CaO-SiO2-CaF2 and CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 flux systems[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(2): 1419 − 1432. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.106
[16] 刘政军, 武丹, 苏允海, 等. Al元素对高强钢药芯焊丝焊缝金属组织和性能的影响[J]. 焊接, 2019(4): 60 − 64. [17] 张文钺. 焊接冶金学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1993. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 张八虎,陈庆城,杨利,陈天云. 自动埋弧焊在压力容器焊接工艺中的应用探析. 中国机械. 2024(01): 38-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 司广全,李太江,李巍,孙琦. 水电工程1000 MPa等级超高强钢埋弧自动焊接头显微组织及力学性能研究. 热力发电. 2024(11): 47-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: