Influence of membrane induced stress on internal stress of oxide film and substrate metal
-
摘要:目的
旨在了解氧化膜所产生的裂尖膜致应力对表面缺陷和应力腐蚀开裂历程中所带来的力学影响规律。
方法以镍基合金600为研究对象,建立SCC全寿命周期膜致应力有限元模型,得出不同ΔT下膜致应力对氧化膜和基体金属裂尖力学场的影响。
结果氧化膜内产生的压应力给基体金属裂尖带来附加拉应力,这个拉应力为膜致应力,加速了氧化膜的破裂;随着温度的升高,氧化膜和基体金属中的膜致应力均增大,但氧化膜内的应力增幅大于基体金属裂尖;在氧化膜和基体金属界面处,Mises应力和拉伸应力都发生了阶跃现象,提升了裂尖的SCC敏感度。
结论膜致应力在裂纹萌生初期的作用不可被忽略,会造成膜的破裂和基体金属的裸露,引起微裂纹的形核和扩展。
Abstract:[Objective] The purpose was to understand mechanical effects of crack tip film induced stress generated by oxide film on surface defects and stress corrosion cracking processes. [Methods] Taking nickel based alloy 600 as the research object, a finite element model of SCC full life cycle film induced stress was established, and influence of film induced stress on mechanical field of oxide film and matrix metal crack tip under different ΔT was obtained. [Results] Compressive stress generated within oxide film brought additional tensile stress to crack tip of substrate metal, which was film induced stress and accelerated rupture of oxide film. As temperature increased, film induced stress in both oxide film and substrate metal increased, but stress increase in oxide film was greater than that at the crack tip of substrate metal. At the interface between oxide film and substrate metal, both Mises stress and tensile stress exhibited a step phenomenon, which enhanced SCC sensitivity of crack tip. [Conclusion] The role of membrane induced stress in early stage of crack initiation couldn’t be ignored, it could cause membrane rupture and exposure of substrate metal, leading to nucleation and propagation of microcracks.
-
Keywords:
- oxide film /
- substrate metal /
- membrane induced stress /
- crack tip
-
0. 前言
镍基合金在高温高压及辐射环境中具有很好的热稳定性和高温强度比,并且具有良好的耐腐蚀性,因此,核电轻水反应堆中的重要结构材料大量使用了镍基合金[1 − 2]。镍基合金良好的耐腐蚀性是由于其表面会形成一层氧化膜,这层氧化膜可以阻止核电水环境中各种酸性离子对基体金属的侵蚀,从而很好的保护了基体金属[3]。然而,研究和实践均表明:镍基合金在高温高压水环境下很容易发生钝化膜的破裂,并且破裂后的钝化膜很难自愈,致使基体金属失去保护,裸露在复杂的腐蚀环境中;同时,在工作载荷和残余应力的共同作用下,很容易使裸露处的金属产生以应力腐蚀开裂(Stress corrosion cracking, SCC)为代表的环境致裂(Environmentally assisted cracking, EAC)问题[4]。这种SCC会随时间不断扩展,从而使核电的关键结构和部件发生开裂[5]。
李美栓等学者[6]和钱余海等学者[7]发现氧化膜含有两种不同的应力,分别为生长应力和热应力。这两种应力是在核电高温水环境中,氧化膜自身产生的生长应力及温度变化所产生的热应力。氧化膜的最终开裂和剥落,是由自身内应力引发的,特别是在应力形式为拉应力时,氧化膜和基体金属界面出现了贯穿裂纹,从而引发氧化膜的剥落。高富国等学者[8]通过在ABAQUS中建立多层氧化膜模型,发现:在不同层的氧化膜界面处发生了应力突变,同时,在氧化膜镍富集层和Cr2O3层应力值变大,这种突变的应力可能促使氧化膜强度降低从而发生破裂。
该文建立SCC裂纹扩展有限元模型,通过数值模拟实现温度变化时由于金属与氧化物的热膨胀系数不同而产生的热应力,在氧化膜中引入生长应力即膜致应力,研究了膜致应力对氧化膜和基体金属内应力的影响。
1. 有限元模型建立
1.1 几何模型建立
在ABAQUS中建立单边裂纹的宽板模型,试样宽度W=20 mm,长度L=25 mm,膜致应力分别施加在试样的上下两端,如图1(a)所示。模型网格划分采用八节点二次平面应变单元(CPE8),为了使得裂尖的应力分布更为精确,在裂尖处进行了较密的网格划分,整个模型的单元数为3 424个,裂尖区域的观测路径如图1(b)所示。
1.2 材料力学模型
镍基合金为幂硬化材料,大量用于核电设备的关键结构,通常采用R-O关系来表征其应力应变力学模型,如式(1)[9]所示:
$$ \frac{\varepsilon }{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = \frac{\sigma }{{{\sigma _0}}} + \alpha {\left( {\frac{\sigma }{{{\sigma _0}}}} \right)^n} $$ (1) 式中:$\varepsilon $为总应变;$\sigma $为总应力;$\varepsilon_0 $和$\sigma _0 $分别为屈服应变和屈服应力;$\alpha $和n分别为材料的偏移系数和硬化指数。该文采用核电镍基合金600用于基体材料,Cr2O3为氧化膜材料[10 − 11]。表1为镍基合金600的力学性能。
表 1 600合金材料力学性能Table 1. Mechanical properties of 600 alloy materials材料 弹性模量E/GPa 泊松比
v屈服应力$\sigma _0 $/MPa 硬化系数
n偏移系数
α600 190 0 436 5.29 1 Cr2O3 19 0.3 — — 0.001 2. 计算结果及分析
2.1 氧化膜内应力分布
该文选取SCC全寿命周期中裂纹长度为a=1 mm小裂纹,通过数值模拟实现采用改变温度的方法,在氧化膜中引入生长应力,初始温度设为280 ℃[12],在此基础上改变相应的温度,分别为T=281 ℃,T=283 ℃,T=285 ℃和T=287 ℃,表示为温度差则为ΔT=1,ΔT=3,ΔT=5和ΔT=7,并逐个分析了不同温度对氧化膜内和基体裂尖区域的力学变化。提取裂尖前方氧化膜内的应力分布曲线,如图2和图3所示。
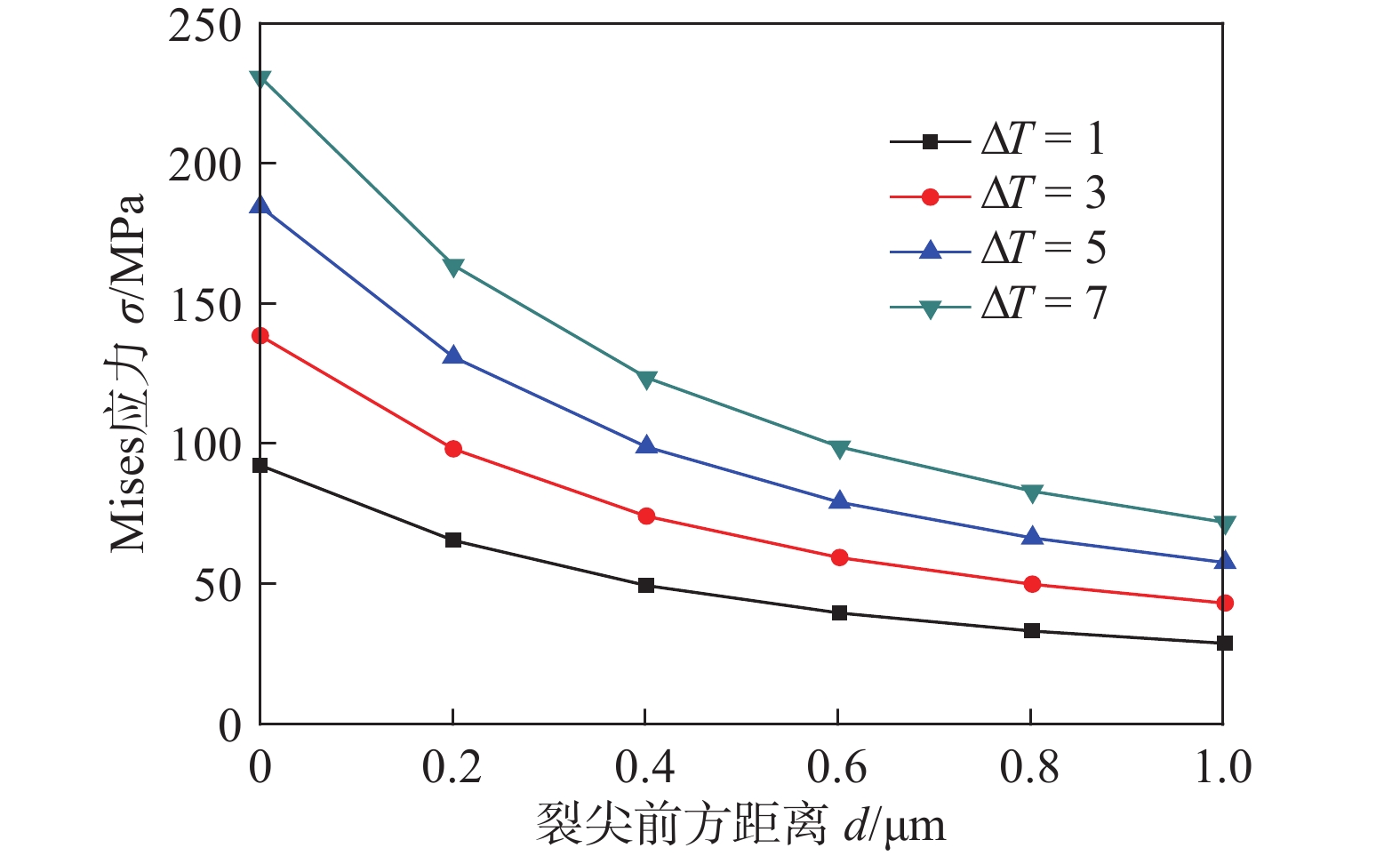
图2为不同ΔT产生的膜内Mises应力曲线。可看出,随着氧化膜裂尖前方距离的增大,膜内Mises应力呈现减小趋势。当ΔT不同时,Mises应力最大值分别为90 MPa,140 MPa,187 MPa和230 MPa;ΔT越大,Mises应力值越大;随着ΔT梯度的增大,膜内应力值增大的梯度大致相等。不同的ΔT下,最小Mises应力均出现在基体金属界面处,并且应力值大小均在50 MPa上下分布。由此可以看出,膜内Mises应力对氧化膜裂尖的影响是最大的。
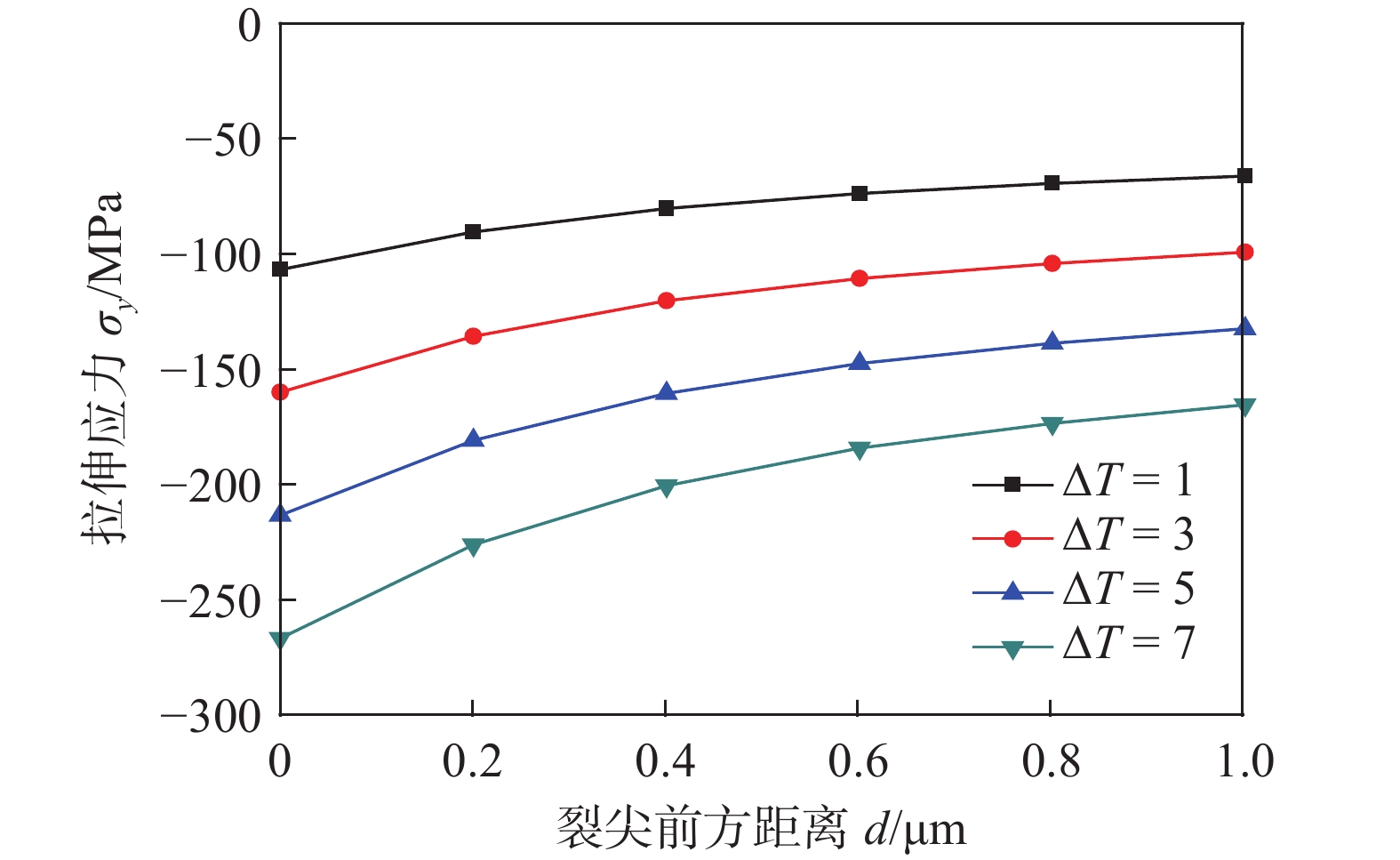
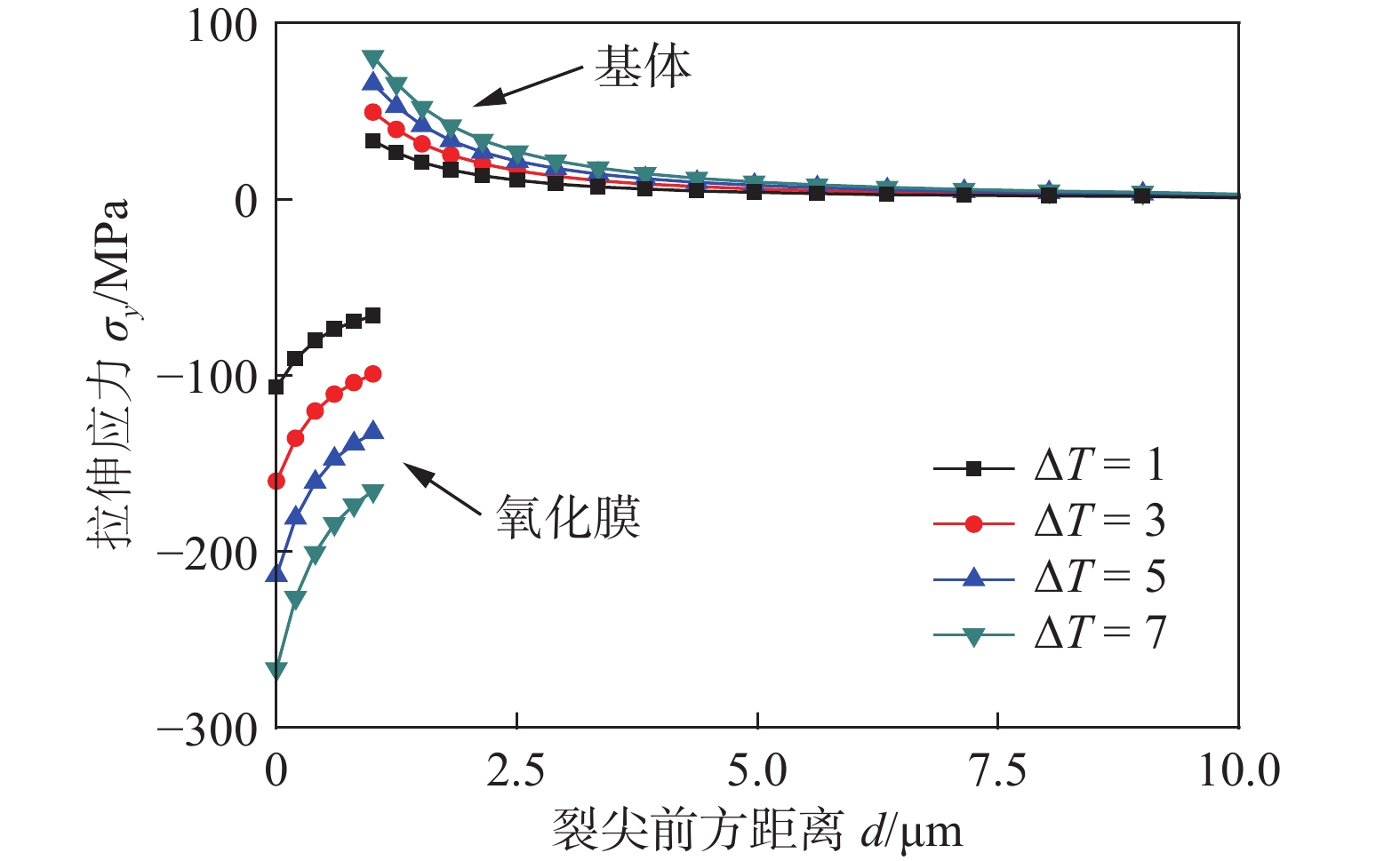
图3为不同ΔT情况下产生的膜内拉伸应力分布曲线。拉伸应力均为负值区域,由此可见,膜内产生的Y向残余应力均为压缩应力。当ΔT不同时,压缩应力最大值分别为110 MPa,160 MPa,220 MPa和270 MPa,不同ΔT对应的压缩应力比Mises应力偏大,说明了Y向残余应力是膜内Mises应力的主要体现形式。最小拉伸应力出现在ΔT=1时的−70 MPa,拉伸应力绝对值高于图2内的最小Mises应力,且增大的绝对值梯度略大于膜内Mises应力增大的梯度,说明了这种复杂的Y向应力给裂纹萌生时期氧化膜的破裂提供有利因素。
2.2 基体金属裂尖应力分布
根据图1(b)中的路径4选取基体金属裂尖前方的部分路径,得出不同ΔT产生的膜致应力对裂尖Mises应力和拉伸应力的影响,如图4和图5所示。
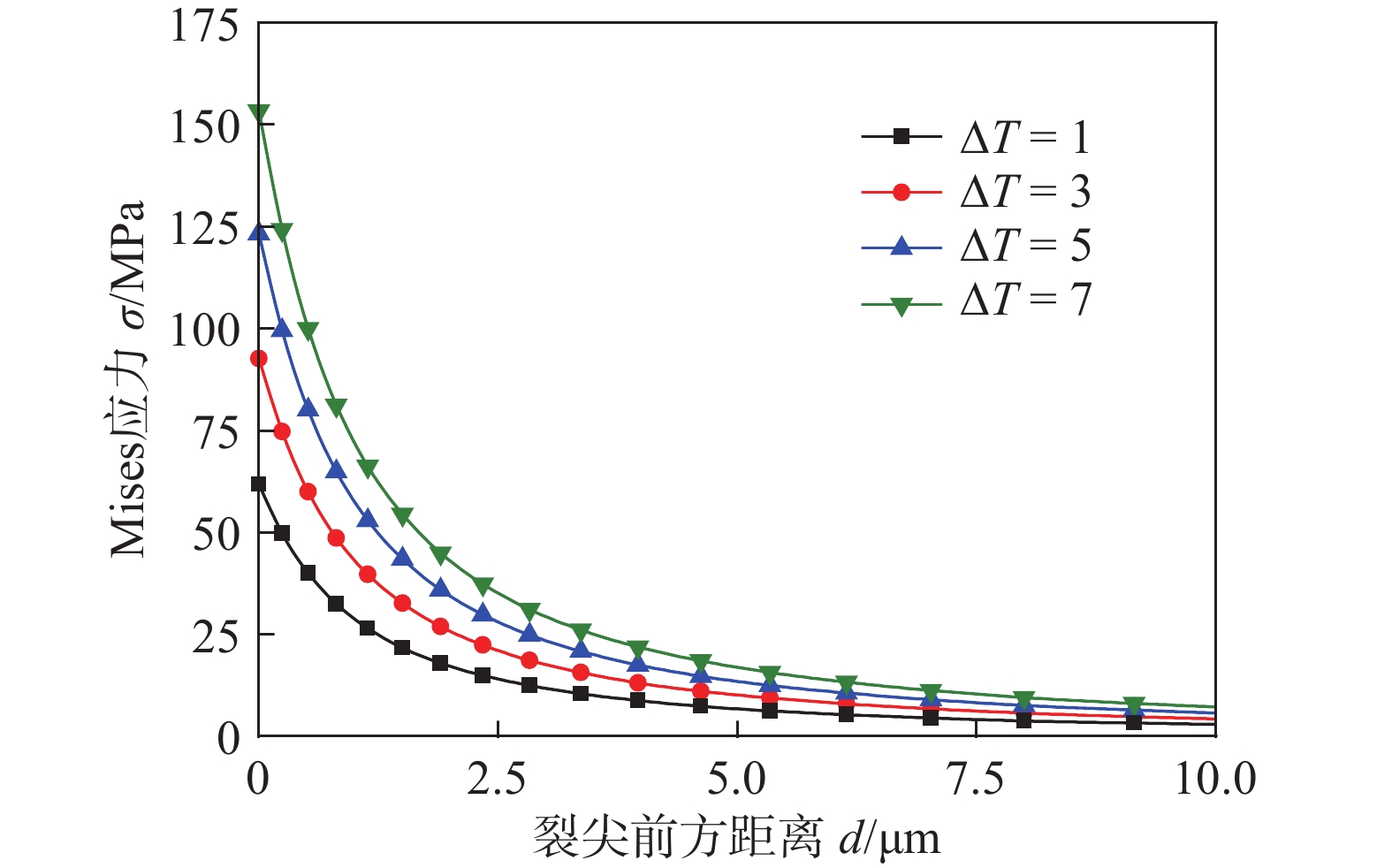
由图4中可以看出,随着ΔT的增大,裂尖产生Mises应力最大值,分别为63 MPa,90 MPa,125 MPa和155 MPa,沿着裂尖前方Mises应力逐渐减小,最终趋于零,说明了膜致应力对基体金属的力学影响仅仅停留在基体金属裂尖区域,这也表明:膜致应力对萌生时期的裂纹作用机制研究具有重要的意义。
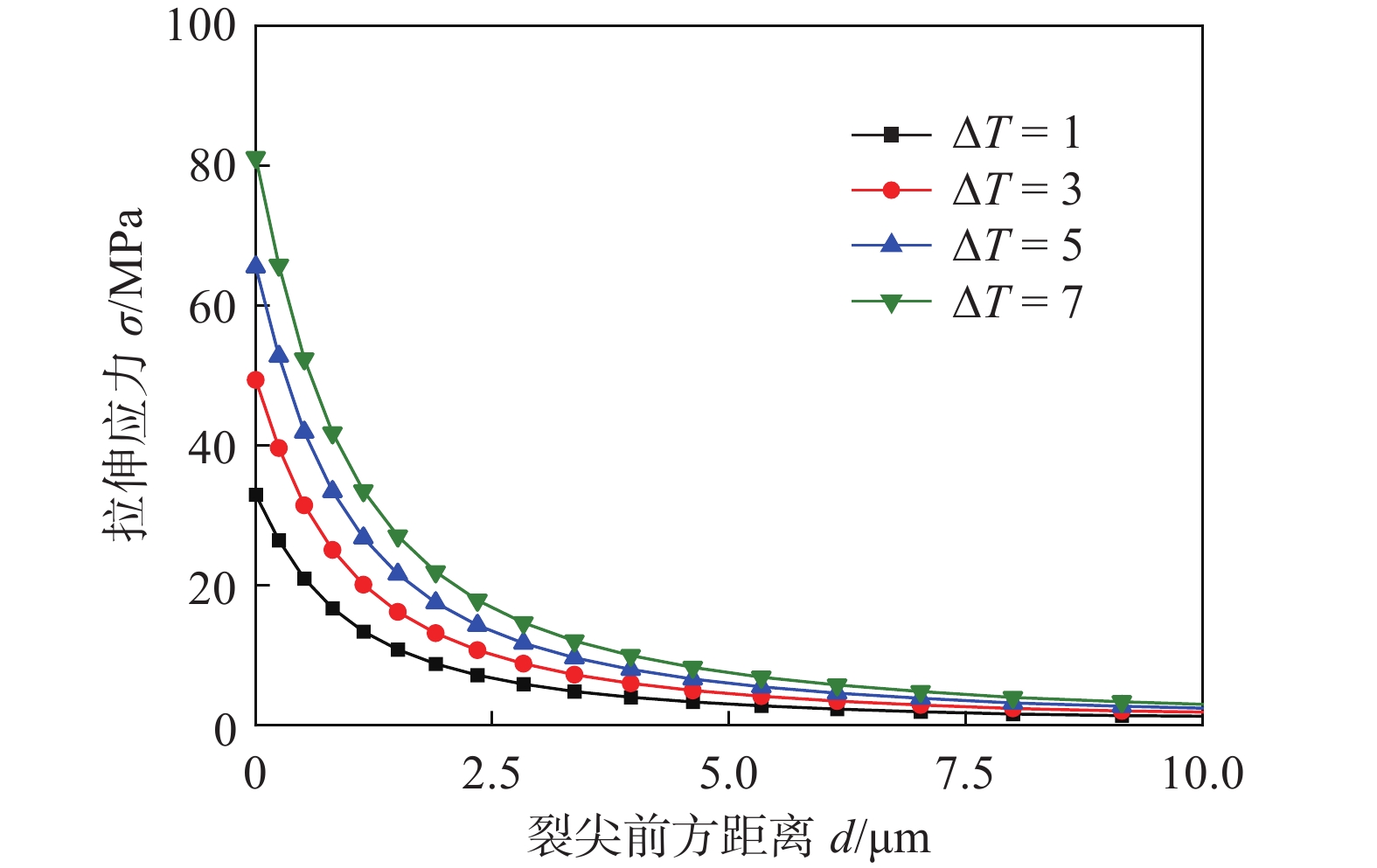
由图5可以看出,随着ΔT的增大,裂尖拉伸应力逐渐增大,与基体金属裂尖Mises应力不同的是,拉伸应力的增大幅度比Mises应力增大幅度小,每组ΔT下的裂尖拉伸应力均出现在裂尖前方,且随着ΔT变大,拉伸应力也越来越大。
2.3 氧化膜和基体金属内应力综合分析
根据图1(b)中的路径4提取裂尖前方Mises应力和拉伸应力曲线,在图6中,首先看到氧化膜内的裂尖应力均大于对应ΔT下基体裂尖应力,膜内最低Mises应力也大于基体内的最小应力。值得注意的是,氧化膜应力的产生,导致氧化膜和基体金属界面处出现了应力的阶跃现象,由于氧化膜是脆性的,而基体金属镍基合金600属于弹塑性材料,两者材料对于应力的敏感度不同,所以出现了阶跃现象。当ΔT=7时,处于氧化膜和基体界面处的Mises应力从50 MPa增大到150 MPa,增大了两倍,说明界面处的应力变化非常大;而当ΔT=1时,界面处的应力由25 MPa增大到65 MPa左右,应力增大1.5倍左右,说明ΔT越大对于界面的应力阶跃越加明显。
图7中拉伸应力曲线也出现了应力的突变。可以看出,在膜内,Y向拉伸应力由压应力突变为基体内的正应力;而在不同的ΔT下,膜内压缩应力分布梯度很明显比基体金属内的拉应力分布梯度大,说明氧化膜应力对膜内的Y向应力具有比基体内产生更明显的效果。这种膜内压缩应力的产生,根据力学平衡导致基体内被迫产生了拉应力,基体裂尖处产生的拉应力就是膜致应力最为显著的具体体现。这种力学分布状态,使得氧化膜和基体金属界面处很容易发生氧化膜的开裂和基体金属裂尖的塑性变形。对于裂纹萌生的初期,膜致应力产生的复杂力学特性使得裂尖对于SCC敏感度大幅提升,膜致应力在裂纹萌生初期的作用不可被忽略。
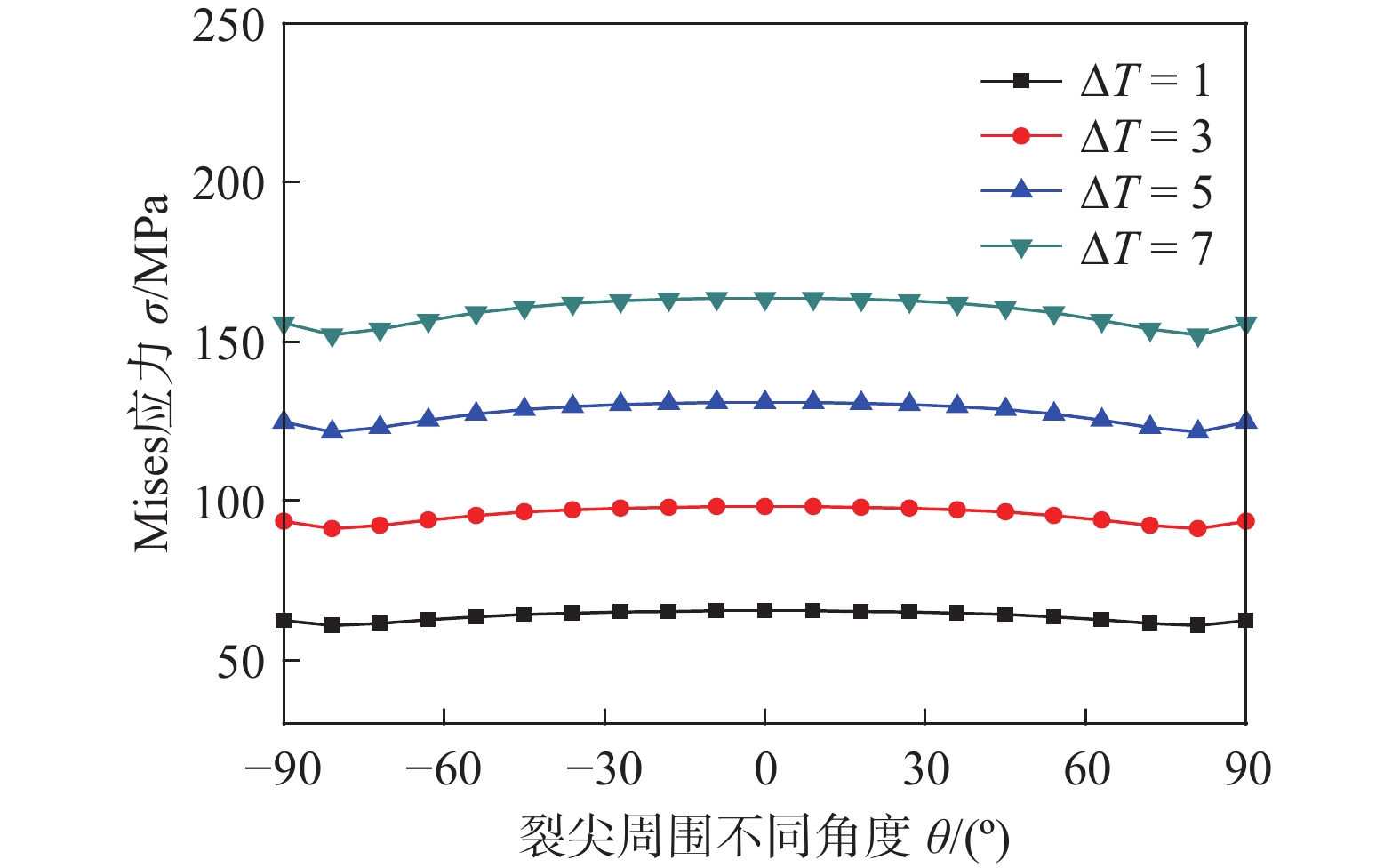
根据图1(b)中的路径1,提取氧化膜表面的Mises应力曲线,如图8所示。可以看出,不同ΔT的最大应力均出现在0°方向上,但是从−90°方向到90°向,应力总体变化不大,趋向于均匀分布,说明氧化膜裂尖处的表面应力沿半圆弧较为均匀的分布;同时,随着ΔT的增大,应力也随一定的梯度增大。
图1(b)中的路径2是氧化膜和基体金属界面靠近氧化膜一侧的半圆形观测路径,路径2上的Mises应力分布如图9所示。可以看出,在0°方向上是应力最低的区域,而在−90°方向和90°方向上应力最大。对比图8可知,氧化膜表面上的应力远大于膜内的其他位置,意味着处于氧化膜裂尖的应力对于评估膜的破裂具有重要意义。
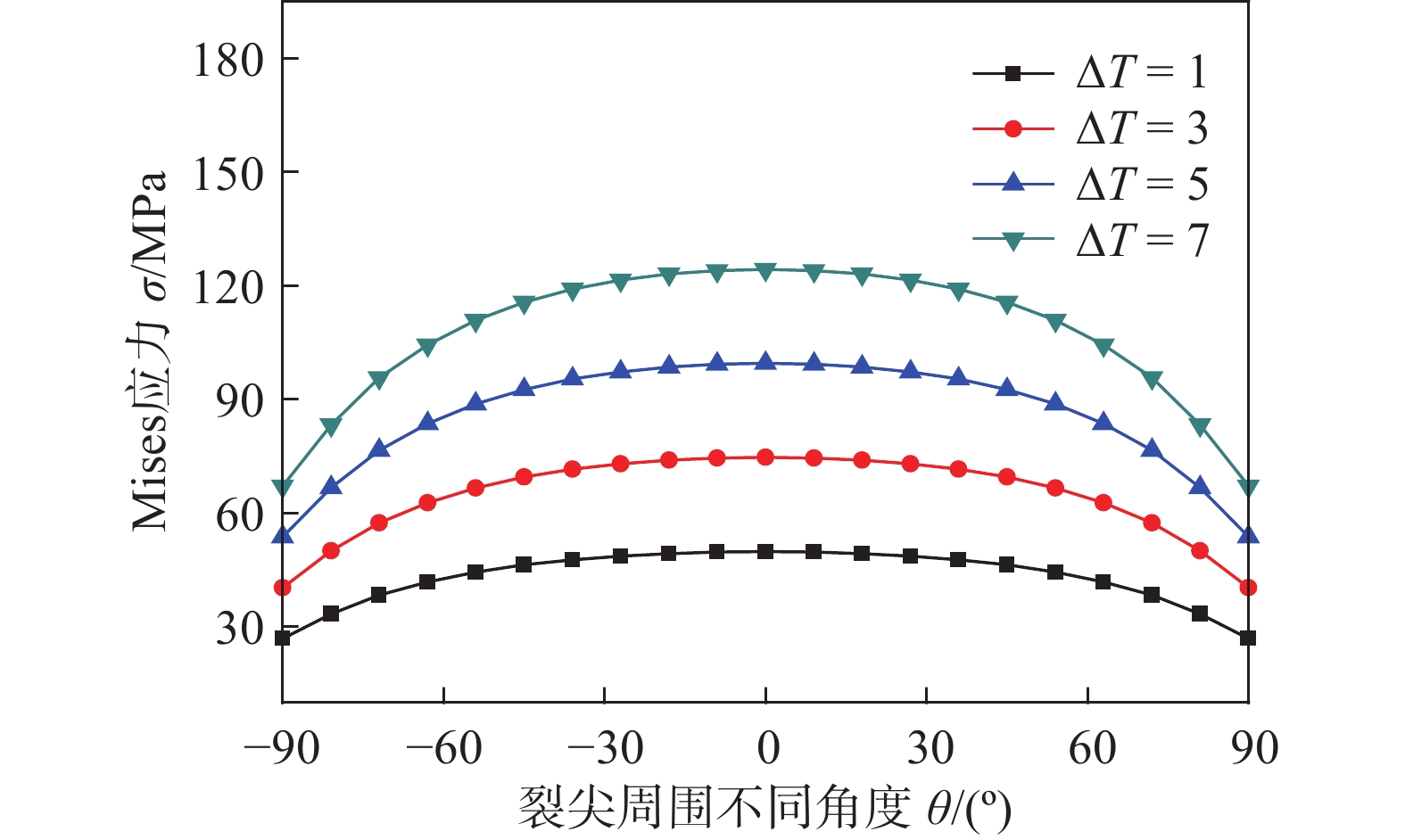
图1(b)中的路径3是氧化膜和基体金属界面靠近基体裂尖一侧的半圆形观测路径,图10是路径3上的应力分布曲线。在基体裂尖一侧,沿着路径3顺时针方向看,应力首先慢慢变大,0°方向上应力最大,接下来应力又逐渐减小,总体呈半圆弧形状分布。基体裂尖0°方向最大应力,是评价裂纹扩展的重要因素。
3. 结论
(1)在膜致应力有限元模型中,通过给表面氧化膜区域加入温度场来引入氧化膜内应力,氧化膜内产生的压应力会给基体金属裂尖带来附加拉应力,这个拉应力为膜致应力,加速了氧化膜的破裂。
(2)膜致应力沿裂尖半圆均匀分布,最大值出现在基体金属裂尖处,随着温度的增大,应力均增大,氧化膜内的应力增幅大于基体金属裂尖,最大应力均出现在各自裂尖区域。
(3)在氧化膜和基体金属界面处,Mises应力和拉伸应力都发生了阶跃现象,这种力学分布状态,使得氧化膜易于开裂,对于裂纹萌生的初期,膜致应力产生的复杂力学特性使得裂尖对于SCC敏感度大幅提升,膜致应力在裂纹萌生初期的作用不可被忽略。
-
表 1 600合金材料力学性能
Table 1 Mechanical properties of 600 alloy materials
材料 弹性模量E/GPa 泊松比
v屈服应力$\sigma _0 $/MPa 硬化系数
n偏移系数
α600 190 0 436 5.29 1 Cr2O3 19 0.3 — — 0.001 -
[1] 李海东. 核电接管安全端镍基690合金微观组织和耐腐蚀性研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018. Lee Haedong. Investigation on microstructure and corrosion resistance of nickel based alloy 690 of nuclear pressure vessel and safe end[D]. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2018.
[2] 段振刚, 潘向烽, 张乐福, 等. 压水堆一回路水中锌含量对镍基690合金氧化膜的影响[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2014, 35(4): 348 − 351. Duan Zhengang, Pan Xiangfeng, Zhang Lefu, et al. Effects of zinc concentration on oxide films of alloy 690 in PWR primary water[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2014, 35(4): 348 − 351.
[3] 付倩南. 镍基合金氧化膜中空位形成机理的第一性原理研究[D]. 湖南湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2021. Fu Qianlan. First principles study on vacancy formation mechanism in oxide film of nickel based alloy [D]. Xiangtan, Hunan, China: Xiangtan University, 2021.
[4] Andresen P L, Gott K, Nelson J L. Stress corrosion cracking of sensitized type 304 stainless steel in 288 ℃ water: a five laboratory round bobbin[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Environmental Degradation of Material in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors, Newport Beach, USA, 1999: 423-433.
[5] Ford P. Mechanisms of environmentally-assisted cracking[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 1989, 40(55): 343 − 362.
[6] 李美栓, 辛丽, 钱余海, 等. 氧化膜应力研究进展[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 1999, 11(5): 300 − 305. Li Meishuan, Xin Li, Qian Yuhai, et al. A review on studies of internal stress in oxide scales[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 1999, 11(5): 300 − 305.
[7] 钱余海, 李美栓, 张亚明. 氧化膜开裂和剥落行为[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2003, 15(2): 90 − 93. Qian Yuhai, Li Meishuan, Zhang Yaming. Cracking and spalling behavior of thin oxide scale[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2003, 15(2): 90 − 93.
[8] 高富国, 薛河, 王耀宇, 等. 多层氧化膜应力腐蚀开裂裂尖的微观力学特性[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2017, 38(8): 578 − 582, 588. Gao Fuguo, Xue He, Wang Yaoyu, et al. Micromechanical characteristics of SCC crack tip in multilayer oxide film[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2017, 38(8): 578 − 582, 588.
[9] Ueda Y, Shi Y, Sun S, et al. Effect of crack depth and strength mis-matching on the relation between J-integral and CTOD for welded tensile specimens(mechanics, strength & structure design)[J]. Transaction of JWRI, 1997, 26(1): 133 − 140.
[10] 檀玉, 梁可心, 张胜寒. 光电化学法研究316L不锈钢在高温水中生成氧化膜的半导体性质[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2013, 33(6): 491 − 495. Tan Yu, Liang Kexin, Zhang Shenhan. Photo-electrochemical study on semiconductor properties of oxide films formed on 316L stainless steel in high temperature water[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2013, 33(6): 491 − 495.
[11] Lu Y H, Peng Q J, Sato T, et al. An ATEM study of oxidation behavior of SCC crack tips in 304L stainless steel in high temperature oxygenated water[J]. Journal of Nuclear Material, 2005, 347: 52 − 68.
[12] 潘品李, 钟约先, 马庆贤, 等. 大型核电主管道制造技术的发展[J]. 锻压装备与制造技术, 2011, 46(1): 13 − 17. Pan Pinli, Zhong Yuexian, Ma Qingxian, et al. Development of manufacturing technology for main pipe of large-sized nuclear power[J]. China Metalforming Equipment & Manufacturing Technology, 2011, 46(1): 13 − 17.





 下载:
下载: